About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 444 results simulation clear search
A Multi-Agent Simulation Approach to Farmland Auction Markets
James Nolan | Published Wednesday, June 22, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This model explores the effects of agent interaction, information feedback, and adaptive learning in repeated auctions for farmland. It gathers information for three types of sealed-bid auctions, and one English auction and compares the auctions on the basis of several measures, including efficiency, price information revelation, and ability to handle repeated bidding and agent learning.
A simulation tool for capability-based team task allocation in emergency-responce environments
Afsaneh Fatemi | Published Wednesday, March 16, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Its a multi agent simulation environment, provided using JADE/Java. It gets the number of agents and tasks, then divides the physical environment to some segments, and then runs a greedy capability-based coalition formation and task allocation algorithm to assign tasks to groups of agents and complete the tasks.
John Q. Public (JQP): A Model of Political Judgment and Behavior
Sung-Youn Kim | Published Monday, March 14, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The model integrates major theories of political judgment and behavior within the classical cognitive paradigm embedded in the ACT-R cognitive architecture. It models preferences and beliefs of political candidates, parties, and groups.
ManPraSim: A Management Practice Simulation
peer-olaf_siebers | Published Wednesday, February 23, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This simulation model is associated with the journal paper “A First Approach on Modelling Staff Proactiveness in Retail Simulation Models” to appear in the Journal of Artificial Societies and Social Simulation 14 (2) 2. The authors are Peer-Olaf Siebers ([email protected]) and Uwe Aickelin ([email protected]).
CROSS - crowd behaviour modelling: a festival crowd model
Nanda Wijermans | Published Monday, February 14, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013CROwd Simulation of Situated individuals represents a modern generation simulation as a (social) scientific tool for understanding crowd behaviour. The CROSS model represents individuals in a crowd as social-cognitive agents that are affected by their social and physical surroundings and produce behaviour and behaviour patterns.
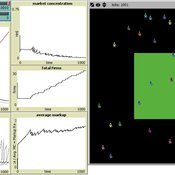
Toward Market Structure as a Complex System: A Web Based Simulation Assignment Implemented in Netlogo
Timothy Kochanski | Published Monday, February 14, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This is the model for a paper that is based on a simulation model, programmed in Netlogo, that demonstrates changes in market structure that occur as marginal costs, demand, and barriers to entry change. Students predict and observe market structure changes in terms of number of firms, market concentration, market price and quantity, and average marginal costs, profits, and markups across the market as firms innovate. By adjusting the demand growth and barriers to entry, students can […]
A simulation of the structure of academic science
Nigel Gilbert | Published Friday, December 31, 2010 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This is a re-implementation of the model described in Gilbert, Nigel. (1997). A simulation of the structure of academic science. Sociological Research Online, 2(2)3, http://www.socresonline.org.uk/
SBH trust model
Di Wang | Published Tuesday, December 14, 2010 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This is a computational model to articulate the theory and test some assumption and axioms for the trust model and its relationship to SBH.
An agent based simulation and data mining framework for scenario analysis of technology products
Moeed Haghnevis | Published Monday, December 13, 2010 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The objective of this study is to create a framework to simulate and analyze the effect of multiple business scenarios on the adoption behavior of a group of technology products.
Agent Based Simulation of Technology Adoption
Moeed Haghnevis | Published Tuesday, December 07, 2010 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The purpose of this model is to study effect of a particular kind of spatial externality, “fashion effect”, on the dynamics of technology diffusion among rational adopters with uncertainty about the p
Displaying 10 of 444 results simulation clear search