About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 521 results for "Jingjing Cai" clear search
Peer reviewed MHMSLeptoDy (Multi-host, multi-serovar Leptospira Dynamics Model)
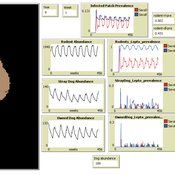
Aniruddha Belsare Matthew Gompper Meghan Mason Claudia Munoz-Zanzi | Published Tuesday, January 29, 2019 | Last modified Tuesday, March 12, 2019Leptospirosis is a neglected, bacterial zoonosis with worldwide distribution, primarily a disease of poverty. More than 200 pathogenic serovars of Leptospira bacteria exist, and a variety of species may act as reservoirs for these serovars. Human infection is the result of direct or indirect contact with Leptospira bacteria in the urine of infected animal hosts, primarily livestock, dogs, and rodents. There is increasing evidence that dogs and dog-adapted serovar Canicola play an important role in the burden of leptospirosis in humans in marginalized urban communities. What is needed is a more thorough understanding of the transmission dynamics of Leptospira in these marginalized urban communities, specifically the relative importance of dogs and rodents in the transmission of Leptospira to humans. This understanding will be vital for identifying meaningful intervention strategies.
One of the main objectives of MHMSLeptoDy is to elucidate transmission dynamics of host-adapted Leptospira strains in multi-host system. The model can also be used to evaluate alternate interventions aimed at reducing human infection risk in small-scale communities like urban slums.
Peer reviewed An extended replication of Abelson's and Bernstein's community referendum simulation
Klaus G. Troitzsch | Published Friday, October 25, 2019 | Last modified Friday, August 25, 2023This is an extended replication of Abelson’s and Bernstein’s early computer simulation model of community referendum controversies which was originally published in 1963 and often cited, but seldom analysed in detail. This replication is in NetLogo 6.3.0, accompanied with an ODD+D protocol and class and sequence diagrams.
This replication replaces the original scales for attitude position and interest in the referendum issue which were distributed between 0 and 1 with values that are initialised according to a normal distribution with mean 0 and variance 1 to make simulation results easier compatible with scales derived from empirical data collected in surveys such as the European Value Study which often are derived via factor analysis or principal component analysis from the answers to sets of questions.
Another difference is that this model is not only run for Abelson’s and Bernstein’s ten week referendum campaign but for an arbitrary time in order that one can find out whether the distributions of attitude position and interest in the (still one-dimensional) issue stabilise in the long run.
While the world’s total urban population continues to grow, not all cities are witnessing such growth, some are actually shrinking. This shrinkage causes several problems to emerge including population loss, economic depression, vacant properties and the contraction of housing markets. Such problems challenge efforts to make cities sustainable. While there is a growing body of work on study shrinking cities, few explore such a phenomenon from the bottom up using dynamic computational models. To overcome this issue this paper presents an spatially explicit agent-based model stylized on the Detroit Tri-county area, an area witnessing shrinkage. Specifically, the model demonstrates how through the buying and selling of houses can lead to urban shrinkage from the bottom up. The model results indicate that along with the lower level housing transactions being captured, the aggregated level market conditions relating to urban shrinkage are also captured (i.e., the contraction of housing markets). As such, the paper demonstrates the potential of simulation to explore urban shrinkage and potentially offers a means to test polices to achieve urban sustainability.
SiFlo: An Agent-based Model to simulate inhabitants’ behavior during a flood event
Patrick Taillandier Franck Taillandier Pascal Di Maiolo Rasool Mehdizadeh | Published Thursday, July 29, 2021SiFlo is an ABM dedicated to simulate flood events in urban areas. It considers the water flowing and the reaction of the inhabitants. The inhabitants would be able to perform different actions regarding the flood: protection (protect their house, their equipment and furniture…), evacuation (considering traffic model), get and give information (considering imperfect knowledge), etc. A special care was taken to model the inhabitant behavior: the inhabitants should be able to build complex reasoning, to have emotions, to follow or not instructions, to have incomplete knowledge about the flood, to interfere with other inhabitants, to find their way on the road network. The model integrates the closure of roads and the danger a flooded road can represent. Furthermore, it considers the state of the infrastructures and notably protection infrastructures as dyke. Then, it allows to simulate a dyke breaking.
The model intends to be generic and flexible whereas provide a fine geographic description of the case study. In this perspective, the model is able to directly import GIS data to reproduce any territory. The following sections expose the main elements of the model.
Replica of Turchin's (2003) Metaethnic Frontier model
Paul Smaldino | Published Sunday, February 15, 2026In his 2003 book, Historical Dynamics (ch. 4), Turchin describes and briefly analyzes a spatial ABM of his metaethnic frontier theory, which is essentially a formalization of a theory by Ibn Khaldun in the 14th century. In the model, polities compete with neighboring polities and can absorb them into an empire. Groups possess “asabiya”, a measure of social solidarity and a sense of shared purpose. Regions that share borders with other groups will have increased asabiya do to salient us vs. them competition. High asabiya enhances the ability to grow, work together, and hence wage war on neighboring groups and assimilate them into an empire. The larger the frontier, the higher the empire’s asabiya.
As an empire expands, (1) increased access to resources drives further growth; (2) internal conflict decreases asabiya among those who live far from the frontier; and (3) expanded size of the frontier decreases ability to wage war along all frontiers. When an empire’s asabiya decreases too much, it collapses. Another group with more compelling asabiya eventually helps establish a new empire.
Digital divide and opinion formation
Dongwon Lim | Published Friday, November 02, 2012 | Last modified Monday, May 20, 2013This model extends the bounded confidence model of Deffuant and Weisbuch. It introduces online contexts in which a person can deliver his or her opinion to several other persons. There are 2 additional parameters accessibility and connectivity.
SBH trust model
Di Wang | Published Tuesday, December 14, 2010 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This is a computational model to articulate the theory and test some assumption and axioms for the trust model and its relationship to SBH.
An empirical ABM for regional land use/cover change: a Dutch case study
Diego Valbuena | Published Saturday, March 12, 2011 | Last modified Thursday, November 11, 2021This is an empirical model described in http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2010.05.001. The objective of the model is to simulate how the decision-making of farmers/agents with different strategies can affect the landscape structure in a region in the Netherlands.
A simple emulation-based computational model
Carlos M Fernández-Márquez Francisco J Vázquez | Published Tuesday, May 21, 2013 | Last modified Tuesday, February 05, 2019Emulation is one of the simplest and most common mechanisms of social interaction. In this paper we introduce a descriptive computational model that attempts to capture the underlying dynamics of social processes led by emulation.
Societal Simulator v203
Tim Gooding | Published Tuesday, October 01, 2013 | Last modified Friday, November 28, 2014Designed to capture the evolutionary forces of global society.
Displaying 10 of 521 results for "Jingjing Cai" clear search