About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 46 results Adaptation clear search
Peer reviewed SequiaBasalto model
Marco Janssen Irene Perez Ibarra Pierre Bommel Diego J. Soler-Navarro Alicia Tenza Peral Francisco Dieguez Cameroni | Published Friday, May 26, 2023This is a replication of the SequiaBasalto model, originally built in Cormas by Dieguez Cameroni et al. (2012, 2014, Bommel et al. 2014 and Morales et al. 2015). The model aimed to test various adaptations of livestock producers to the drought phenomenon provoked by climate change. For that purpose, it simulates the behavior of one livestock farm in the Basaltic Region of Uruguay. The model incorporates the price of livestock, fodder and paddocks, as well as the growth of grass as a function of climate and seasons (environmental submodel), the life cycle of animals feeding on the pasture (livestock submodel), and the different strategies used by farmers to manage their livestock (management submodel). The purpose of the model is to analyze to what degree the common management practices used by farmers (i.e., proactive and reactive) to cope with seasonal and interannual climate variations allow to maintain a sustainable livestock production without depleting the natural resources (i.e., pasture). Here, we replicate the environmental and livestock submodel using NetLogo.
One year is 368 days. Seasons change every 92 days. Each day begins with the growth of grass as a function of climate and season. This is followed by updating the live weight of cows according to the grass height of their patch, and grass consumption, which is determined based on the updated live weight. After consumption, cows grow and reproduce, and a new grass height is calculated. Cows then move to the patch with less cows and with the highest grass height. This updated grass height value will be the initial grass height for the next day.
Agent based modeling of the effects of carbon payments and forest owner cooperatives on carbon storage and revenue in Pacific Northwest forestlands.
Dan Brown Pranab Roy Chowdhury | Published Tuesday, May 09, 2023The Olympic Peninsula ABM works as a virtual laboratory to simulate the existing forestland management practices as followed by different forestland owner groups in the Olympic Peninsula, Washington, and explore how they could shape the future provisions of multifunctional ecosystem services such as Carbon storage and revenue generation under the business-as-usual scenario as well as by their adaptation to interventions. Forestlands are socio-ecological systems that interact with economic, socio-cultural, and policy systems. Two intervention scenarios were introduced in this model to simulate the adaptation of landowner behavior and test the efficacy of policy instruments in promoting sustainable forest practices and fostering Carbon storage and revenue generation. (1) A market-linked carbon offset scheme that pays the forestland owners a financial incentive in the form of a yearly carbon rent. (2) An institutional intervention policy that allows small forest owners (SFLO) to cooperate for increased market access and benefits under carbon rent scenario. The model incorporates the heterogeneous contexts within which the forestland owners operate and make their forest management decisions by parameterizing relevant agent attributes and contextualizing their unique decision-making processes.
NK model for multilevel adaptation
Dario Blanco Fernandez | Published Wednesday, November 30, 2022Previous research on organizations often focuses on either the individual, team, or organizational level. There is a lack of multidimensional research on emergent phenomena and interactions between the mechanisms at different levels. This paper takes a multifaceted perspective on individual learning and autonomous group formation and turnover. To analyze interactions between the two levels, we introduce an agent-based model that captures an organization with a population of heterogeneous agents who learn and are limited in their rationality. To solve a task, agents form a group that can be adapted from time to time. We explore organizations that promote learning and group turnover either simultaneously or sequentially and analyze the interactions between the activities and the effects on performance. We observe underproportional interactions when tasks are interdependent and show that pushing learning and group turnover too far might backfire and decrease performance significantly.
Peer reviewed The Viability of the Social-Ecological Agroecosystem (ViSA) Spatial Agent-based Model
Mostafa Shaaban | Published Friday, June 03, 2022ViSA simulates the decision behaviors of different stakeholders showing demands for ecosystem services (ESS) in agricultural landscape. The lack of sufficient supply of ESSs triggers stakeholders to apply different management options to increase their supply. However, while attempting to reduce the supply-demand gap, conflicts arise among stakeholders due to the tradeoff nature of some ESS. ViSA investigates conditions and scenarios that can minimize such supply-demand gap while reducing the risk of conflicts by suggesting different mixes of management options and decision rules.
Viability analysis of a population submitted to floods
Sophie Martin | Published Wednesday, September 22, 2021This model computes the guaranteed viability kernel of a model describing the evolution of a population submitted to successive floods.
The population is described by its wealth and its adaptation rate to floods, the control are information campaigns that have a cost but increase the adaptation rate and the expected successive floods belong to given set defined by the maximal high and the minimal time between two floods.
Peer reviewed Virus Transmission with Super-spreaders
J M Applegate | Published Saturday, September 11, 2021A curious aspect of the Covid-19 pandemic is the clustering of outbreaks. Evidence suggests that 80\% of people who contract the virus are infected by only 19% of infected individuals, and that the majority of infected individuals faile to infect another person. Thus, the dispersion of a contagion, $k$, may be of more use in understanding the spread of Covid-19 than the reproduction number, R0.
The Virus Transmission with Super-spreaders model, written in NetLogo, is an adaptation of the canonical Virus Transmission on a Network model and allows the exploration of various mitigation protocols such as testing and quarantines with both homogenous transmission and heterogenous transmission.
The model consists of a population of individuals arranged in a network, where both population and network degree are tunable. At the start of the simulation, a subset of the population is initially infected. As the model runs, infected individuals will infect neighboring susceptible individuals according to either homogenous or heterogenous transmission, where heterogenous transmission models super-spreaders. In this case, k is described as the percentage of super-spreaders in the population and the differing transmission rates for super-spreaders and non super-spreaders. Infected individuals either recover, at which point they become resistant to infection, or die. Testing regimes cause discovered infected individuals to quarantine for a period of time.
Multi-Hazard Coastal Agent-Based Model (MHCABM)
Andrew Allison | Published Thursday, August 05, 2021MHCABM is an agent-based, multi-hazard risk interaction model with an integrated applied dynamic adaptive pathways planning component. It is designed to explore the impacts of climate change adaptation decisions on the form and function of a coastal human-environment system, using as a case study an idealised patch based representation of the Mount North-Omanu area of Tauranga city, New Zealand. The interacting hazards represented are erosion, inundation, groundwater intrusion driven by intermittent heavy rainfall / inundations (storm) impacts, and sea level rise.
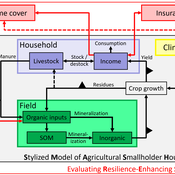
SMASH: Stylized Model of Agricultural Smallholder Households
Tim Williams | Published Tuesday, December 08, 2020The SMASH model is an agent-based model of rural smallholder households. It models households’ evolving income and wealth, which they earn through crop sales. Wealth is carried in the form of livestock, which are grazed on an external rangeland (exogenous) and can be bought/sold as investment/coping mechanisms. The model includes a stylized representation of soil nutrient dynamics, modeling the inflows and outflows of organic and inorganic nitrogen from each household’s field.
The model has been applied to assess the resilience-enhancing effects of two different farm-level adaptation strategies: legume cover cropping and crop insurance. These two strategies interact with the model through different mechanims - legume cover cropping through ecological mechanisms and crop insurance through financial mechanisms. The model can be used to investigate the short- and long-term effects of these strategies, as well as how they may differently benefit different types of household.
The Internal Organizational Plasticity Model (IOP 2.1.2)
Davide Secchi | Published Tuesday, June 02, 2020IOP 2.1.2 is an agent-based simulation model designed to explore the relations between (1) employees, (2) tasks and (3) resources in an organizational setting. By comparing alternative cognitive strategies in the use of resources, employees face increasingly demanding waves of tasks that derive by challenges the organization face to adapt to a turbulent environment. The assumption tested by this model is that a successful organizational adaptation, called plastic, is necessarily tied to how employees handle pressure coming from existing and new tasks. By comparing alternative cognitive strategies, connected to ‘docility’ (Simon, 1993; Secchi, 2011) and ‘extended’ cognition (Clark, 2003, Secchi & Cowley, 2018), IOP 2.1.2 is an attempt to indicate which strategy is most suitable and under which scenario.
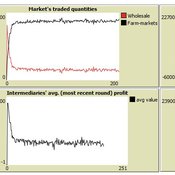
Market-level effects of firm-level adaptation and intermediation in networked markets of fresh foods: a case study in Colombia.
César García-Díaz | Published Sunday, April 12, 2020 | Last modified Sunday, April 12, 2020This a model developed as a part of the paper Mejía, G. & García-Díaz, C. (2018). Market-level effects of firm-level adaptation and intermediation in networked markets of fresh foods: a case study in Colombia. Agricultural Systems 160: 132-142.
It simulates the competition dynamics of the potato market in Bogotá, Colombia. The model explores the economic impact of intermediary actors on the potato supply chain.
Displaying 10 of 46 results Adaptation clear search