About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 972 results for "M Van Den Hoven" clear search
We provide a theory-grounded, socio-geographic agent-based model to present a possible explanation for human movement in the Adriatic region within the Cetina phenomenon.
Focusing on ideas of social capital theory from Piere Bordieu (1986), we implement agent mobility in an abstract geography based on cultural capital (prestige) and social capital (social position). Agents hold myopic representations of social (Schaff, 2016) and geographical networks and decide in a heuristic way on moving (and where) or staying.
The model is implemented in a fork of the Laboratory for Simulation Development (LSD), appended with GIS capabilities (Pereira et. al. 2020).
SimPLS - The PLS Agent
Iris Lorscheid Sandra Schubring Matthias Meyer Christian Ringle | Published Monday, April 18, 2016 | Last modified Tuesday, May 17, 2016The simulation model SimPLS shows an application of the PLS agent concept, using SEM as empirical basis for the definition of agent architectures. The simulation model implements the PLS path model TAM about the decision of using innovative products.
Demand Planning Model
Iris Lorscheid Jonas Hauke Matthias Meyer | Published Wednesday, October 04, 2017Demand planning requires processing of distributed information. In this process, individuals, their properties and interactions play a crucial role. This model is a computational testbed to investigate these aspects with respect to forecast accuracy.
Kulayinjana
Christophe Le Page Arthur Perrotton Michel De Garine-Wichatitsky Barry Bitu Killion Koyisi Ferdinand Mwamba Cephus Ncube Victor Ncube Siphusisiwe Ndlovu Raphael Ngwenya Ambu Nyathi Fumbane Nyathi Patrick Sibanda Zenzo Sibanda | Published Monday, October 03, 2016a computer-based role-playing game simulating the interactions between farming activities, livestock herding and wildlife in a virtual landscape reproducing local socioecological dynamics at the periphery of Hwange National Park (Zimbabwe).
Alternative scenarios of green consumption in Italy: an empirically grounded model.
Giangiacomo Bravo Elena Vallino Alessandro K Cerutti Maria Beatrice Pairotti | Published Thursday, March 28, 2013 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013We provide a full description of the model following the ODD protocol (Grimm et al. 2010) in the attached document. The model is developed in NetLogo 5.0 (Wilenski 1999).
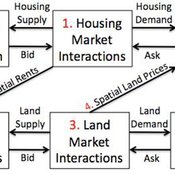
Coupled Housing and Land Markets (CHALMS)
Nicholas Magliocca Virginia Mcconnell Margaret Walls | Published Friday, November 02, 2012 | Last modified Monday, October 27, 2014CHALMS simulates housing and land market interactions between housing consumers, developers, and farmers in a growing ex-urban area.
A simplified Arthur & Polak logic circuit model of combinatory technology build-out via incremental development. Only some inventions trigger radical effects, suggesting they depend on whole interdependent systems rather than specific innovations.
The Urban Drought Nexus Tool
Roger Cremades Muhamad Khairulbahri | Published Thursday, December 14, 2023The “Urban Drought Nexus Tool” is a system dynamics model, aiming to facilitate the co-development of climate services for cities under increasing droughts. The tool integrates multiple types of information and still can be applied to other case studies with minimal adjustments on the parameters of land use, water consumption and energy use in the water sector. The tool needs hydrological projections under climate scenarios to evaluate climatic futures, and requires the co-creation of socio-economic future scenarios with local stakeholders. Thus it is possible to provide specific information about droughts taking into account future water availability and future water consumption. Ultimately, such complex system as formed by the water-energy-land nexus can be reduced to single variables of interest, e.g. the number of events with no water available in the future and their length, so that the complexities are reduced and the results can be conveyed to society in an understandable way, including the communication of uncertainties. The tool and an explanatory guide in pdf format are included. Planned further developments include calibrating the system dynamics model with the social dynamics behind each flow with agent-based models.
LimnoSES - social-ecological lake management undergoing regime shifts
Romina Martin | Published Thursday, November 24, 2016 | Last modified Friday, January 18, 2019LimnoSES is a coupled system dynamics, agent-based model to simulate social-ecological feedbacks in shallow lake use and management.
Peer reviewed MIOvCWD
Aniruddha Belsare | Published Friday, December 13, 2019MIOvCWD is a spatially-explicit, agent-based model designed to simulate the spread of chronic wasting disease (CWD) in Michigan’s white-tailed deer populations. CWD is an emerging prion disease of North American cervids (white-tailed deer Odocoileus virginianus, mule deer Odocoileus hemionus, and elk Cervus elaphus) that is being actively managed by wildlife agencies in most states and provinces in North America, including Michigan. MIOvCWD incorporates features like deer population structure, social organization and behavior that are particularly useful to simulate CWD dynamics in regional deer populations.
Displaying 10 of 972 results for "M Van Den Hoven" clear search