About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers at all levels engage in the establishment and adoption of community standards and good practices for developing and sharing computational models. Model authors can freely publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library alongside narrative documentation, open science metadata, and other emerging open science norms that facilitate software citation, reproducibility, interoperability, and reuse. Model authors can also request peer review of their computational models to receive a DOI.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with additional detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 194 results population clear
Ornstein-Uhlenbeck Pandemic package
Peter Cotton | Published Friday, April 24, 2020 | Last modified Friday, May 08, 2020Pandemic (pip install pandemic)
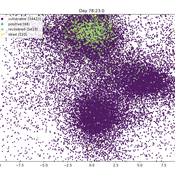
An agent model in which commuting, compliance, testing and contagion parameters drive infection in a population of thousands of millions. Agents follow Ornstein-Uhlenbeck processes in the plane and collisions drive transmission. Results are stored at SwarmPrediction.com for further analysis, and can be retrieved by anyone.
This is a very simple simulation that in a special case can be shown to be approximated by a compartmental model with time varying infection rate.
Peer reviewed NetLogo model of USA mass shootings
Smarzhevskiy Ivan | Published Tuesday, September 24, 2019 | Last modified Tuesday, April 14, 2020Is the mass shooter a maniac or a relatively normal person in a state of great stress? According to the FBI report (Silver, J., Simons, A., & Craun, S. (2018). A Study of the Pre-Attack Behaviors of Active Shooters in the United States Between 2000 – 2013. Federal Bureau of Investigation, U.S. Department of Justice,Washington, D.C. 20535.), only 25% of the active shooters were known to have been diagnosed by a mental health professional with a mental illness of any kind prior to the offense.
The main objects of the model are the humans and the guns. The main factors influencing behavior are the population size, the number of people with mental disabilities (“psycho” in the model terminology) per 100,000 population, the total number of weapons (“guns”) in the population, the availability of guns for humans, the intensity of stressors affecting humans and the threshold level of stress, upon reaching which a person commits an act of mass shooting.
The key difference (in the model) between a normal person and a psycho is that a psycho accumulates stressors and, upon reaching a threshold level, commits an act of mass shooting. A normal person is exposed to stressors, but reaching the threshold level for killing occurs only when the simultaneous effect of stressors on him exceeds this level.
The population dynamics are determined by the following factors: average (normally distributed) life expectancy (“life_span” attribute of humans) and population growth with the percentage of newborns set by the value of the TickReprRatio% slider of the current population volume from 16 to 45 years old.Thus, one step of model time corresponds to a year.
Cultural Spread
Salvador Pardo-Gordó Salvador Pardo Gordó | Published Thursday, April 02, 2015 | Last modified Thursday, April 23, 2020The purpose of the model is to simulate the cultural hitchhiking hypothesis to explore how neutral cultural traits linked with advantageous traits spread together over time
Hybrid Agent-Based and Equation Based Model for Infectious Disease Spread
Elizabeth Hunter Brian Mac Namee John Kelleher | Published Sunday, April 19, 2020Our model is hybrid agent-based and equation based model for human air-borne infectious diseases measles. It follows an SEIR (susceptible, exposed,infected, and recovered) type compartmental model with the agents moving be-tween the four state relating to infectiousness. However, the disease model canswitch back and forth between agent-based and equation based depending onthe number of infected agents. Our society model is specific using the datato create a realistic synthetic population for a county in Ireland. The modelincludes transportation with agents moving between their current location anddesired destination using predetermined destinations or destinations selectedusing a gravity model.
AncientS-ABM: Agent-Based Modeling of Past Societies Social Organization
Angelos Chliaoutakis | Published Thursday, April 09, 2020AncientS-ABM is an agent-based model for simulating and evaluating the potential social organization of an artificial past society, configured by available archaeological data. Unlike most existing agent-based models used in archaeology, our ABM framework includes completely autonomous, utility-based agents. It also incorporates different social organization paradigms, different decision-making processes, and also different cultivation technologies used in ancient societies. Equipped with such paradigms, the model allows us to explore the transition from a simple to a more complex society by focusing on the historical social dynamics; and to assess the influence of social organization on agents’ population growth, agent community numbers, sizes and distribution.
AncientS-ABM also blends ideas from evolutionary game theory with multi-agent systems’ self-organization. We model the evolution of social behaviours in a population of strategically interacting agents in repeated games where they exchange resources (utility) with others. The results of the games contribute to both the continuous re-organization of the social structure, and the progressive adoption of the most successful agent strategies. Agent population is not fixed, but fluctuates over time, while agents in stage games also receive non-static payoffs, in contrast to most games studied in the literature. To tackle this, we defined a novel formulation of the evolutionary dynamics via assessing agents’ rather than strategies’ fitness.
As a case study, we employ AncientS-ABM to evaluate the impact of the implemented social organization paradigms on an artificial Bronze Age “Minoan” society, located at different geographical parts of the island of Crete, Greece. Model parameter choices are based on archaeological evidence and studies, but are not biased towards any specific assumption. Results over a number of different simulation scenarios demonstrate better sustainability for settlements consisting of and adopting a socio-economic organization model based on self-organization, where a “heterarchical” social structure emerges. Results also demonstrate that successful agent societies adopt an evolutionary approach where cooperation is an emergent strategic behaviour. In simulation scenarios where the natural disaster module was enabled, we observe noticeable changes in the settlements’ distribution, relating to significantly higher migration rates immediately after the modeled Theran eruption. In addition, the initially cooperative behaviour is transformed to a non-cooperative one, thus providing support for archaeological theories suggesting that the volcanic eruption led to a clear breakdown of the Minoan socio-economic system.
…
PoliSEA: model of Policy – Social Ecological system Adaptation
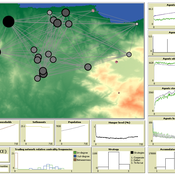
Kirill Orach Maja Schlüter | Published Thursday, March 26, 2020PoliSEA represents a continuous policy process cycle, integrated with the dynamics of a fishery social-ecological system. The policy process in the model is represented by interactions between policymakers and interest groups and subsequent voting during which policymaker decide to increase or decrease the fishing quota for the next season. Policymakers’ positions can be influenced by lobbying of interest groups or interest group coalitions. The quota adopted through the policy process determines the amount of fish that can be harvested from the fish population during the season.
Informal City version 1.0
Nina Schwarz | Published Friday, July 25, 2014 | Last modified Thursday, July 30, 2015InformalCity, a spatially explicit agent-based model, simulates an artificial city and allows for testing configurations of urban upgrading schemes in informal settlements.
Exploring Urban Shrinkage
Andrew Crooks | Published Thursday, March 19, 2020While the world’s total urban population continues to grow, this growth is not equal. Some cities are declining, resulting in urban shrinkage which is now a global phenomenon. Many problems emerge due to urban shrinkage including population loss, economic depression, vacant properties and the contraction of housing markets. To explore this issue, this paper presents an agent-based model stylized on spatially explicit data of Detroit Tri-county area, an area witnessing urban shrinkage. Specifically, the model examines how micro-level housing trades impact urban shrinkage by capturing interactions between sellers and buyers within different sub-housing markets. The stylized model results highlight not only how we can simulate housing transactions but the aggregate market conditions relating to urban shrinkage (i.e., the contraction of housing markets). To this end, the paper demonstrates the potential of simulation to explore urban shrinkage and potentially offers a means to test polices to alleviate this issue.
Artificial Long House Valley-Black Mesa
Amy Warren Lisa Sattenspiel | Published Thursday, March 19, 2020This model is an extension of the Artificial Long House Valley (ALHV) model developed by the authors (Swedlund et al. 2016; Warren and Sattenspiel 2020). The ALHV model simulates the population dynamics of individuals within the Long House Valley of Arizona from AD 800 to 1350. Individuals are aggregated into households that participate in annual agricultural and demographic cycles. The present version of the model incorporates features of the ALHV model including realistic age-specific fertility and mortality and, in addition, it adds the Black Mesa environment and population, as well as additional methods to allow migration between the two regions.
As is the case for previous versions of the ALHV model as well as the Artificial Anasazi (AA) model from which the ALHV model was derived (Axtell et al. 2002; Janssen 2009), this version makes use of detailed archaeological and paleoenvironmental data from the Long House Valley and the adjacent areas in Arizona. It also uses the same methods as the original AA model to estimate annual maize productivity of various agricultural zones within the Long House Valley. A new environment and associated methods have been developed for Black Mesa. Productivity estimates from both regions are used to determine suitable locations for households and farms during each year of the simulation.
This model extends the original Artifical Anasazi (AA) model to include individual agents, who vary in age and sex, and are aggregated into households. This allows more realistic simulations of population dynamics within the Long House Valley of Arizona from AD 800 to 1350 than are possible in the original model. The parts of this model that are directly derived from the AA model are based on Janssen’s 1999 Netlogo implementation of the model; the code for all extensions and adaptations in the model described here (the Artificial Long House Valley (ALHV) model) have been written by the authors. The AA model included only ideal and homogeneous “individuals” who do not participate in the population processes (e.g., birth and death)–these processes were assumed to act on entire households only. The ALHV model incorporates actual individual agents and all demographic processes affect these individuals. Individuals are aggregated into households that participate in annual agricultural and demographic cycles. Thus, the ALHV model is a combination of individual processes (birth and death) and household-level processes (e.g., finding suitable agriculture plots).
As is the case for the AA model, the ALHV model makes use of detailed archaeological and paleoenvironmental data from the Long House Valley and the adjacent areas in Arizona. It also uses the same methods as the original model (from Janssen’s Netlogo implementation) to estimate annual maize productivity of various agricultural zones within the valley. These estimates are used to determine suitable locations for households and farms during each year of the simulation.
Displaying 10 of 194 results population clear