About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers at all levels engage in the establishment and adoption of community standards and good practices for developing and sharing computational models. Model authors can freely publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library alongside narrative documentation, open science metadata, and other emerging open science norms that facilitate software citation, reproducibility, interoperability, and reuse. Model authors can also request peer review of their computational models to receive a DOI.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with additional detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 136 results #Networks clear search
Simulating Sustainability of Collective Awareness Platform for Sustainability and Social Innovation (CAPS)
Peter Gerbrands | Published Friday, May 08, 2020In an associated paper which focuses on analyzing the structure of several egocentric networks of collective awareness platforms for sustainable innovation (CAPS), this model is developed. It answers the question whether the network structure is determinative for the sustainability of the created awareness. Based on a thorough literature review a model is developed to explain and operationalize the concept of sustainability of a social network in terms of importance, effectiveness and robustness. By developing this agent-based model, the expected outcomes after the dissolution of the CAPS are predicted and compared with the results of a network with the same participants but with different ties. Twitter data from different CAPS is collected and used to feed the simulation. The results show that the structure of the network is of key importance for its sustainability. With this knowledge and the ability to simulate the results after network changes have taken place, CAPS can assess the sustainability of their legacy and actively steer towards a longer lasting potential for social innovation. The retrieved knowledge urges organizations like the European Commission to adopt a more blended approach focusing not only on solving societal issues but on building a community to sustain the initiated development.
Reflexivity in a diffusion of innovations model
César García-Díaz Carlos Cordoba | Published Thursday, May 07, 2020In this agent-based model, agents decide to adopt a new product according to a utility function that depends on two kinds of social influences. First, there is a local influence exerted on an agent by her closest neighbors that have already adopted, and also by herself if she feels the product suits her personal needs. Second, there is a global influence which leads agents to adopt when they become aware of emerging trends happening in the system. For this, we endow agents with a reflexive capacity that allows them to recognize a trend, even if they can not perceive a significant change in their neighborhood.
Results reveal the appearance of slowdown periods along the adoption rate curve, in contrast with the classic stylized bell-shaped behavior. Results also show that network structure plays an important role in the effect of reflexivity: while some structures (e.g., scale-free networks) may amplify it, others (e.g., small-world structure) weaken such an effect.
Exploring the Effects of Link Recommendations on Social Networks
Andrew Crooks Ciara Sibley | Published Thursday, March 19, 2020The purpose of this model is explore how “friend-of-friend” link recommendations, which are commonly used on social networking sites, impact online social network structure. Specifically, this model generates online social networks, by connecting individuals based upon varying proportions of a) connections from the real world and b) link recommendations. Links formed by recommendation mimic mutual connection, or friend-of-friend algorithms. Generated networks can then be analyzed, by the included scripts, to assess the influence that different proportions of link recommendations have on network properties, specifically: clustering, modularity, path length, eccentricity, diameter, and degree distribution.
Emergence of Small-World Networks in an Overlapping-Generations Model of Social Dynamics, Trust and Economic Performance
Bogumił Kamiński Jakub Growiec Katarzyna Growiec | Published Thursday, February 27, 2020We study the impact of endogenous creation and destruction of social ties in an artificial society on aggregate outcomes such as generalized trust, willingness to cooperate, social utility and economic performance. To this end we put forward a computational multi-agent model where agents of overlapping generations interact in a dynamically evolving social network. In the model, four distinct dimensions of individuals’ social capital: degree, centrality, heterophilous and homophilous interactions, determine their generalized trust and willingness to cooperate, altogether helping them achieve certain levels of social utility (i.e., utility from social contacts) and economic performance. We find that the stationary state of the simulated social network exhibits realistic small-world topology. We also observe that societies whose social networks are relatively frequently reconfigured, display relatively higher generalized trust, willingness to cooperate, and economic performance – at the cost of lower social utility. Similar outcomes are found for societies where social tie dissolution is relatively weakly linked to family closeness.
City Sandbox
Javier Sandoval | Published Thursday, January 09, 2020This model grows land use patterns that emerge as a result of land-use compatibilities stablished in urban development plans, land topography, and street networks. It contains urban brushes to paint streets and land uses as a way to learn about urban pattern emergence through free experimentation.
Managing networked landscapes: conservation in fragmented, regionally connected world
Jacopo A. Baggio Michael Schoon Sechindra Vallury | Published Monday, December 09, 2019Exploring how learning and social-ecological networks influence management choice set and their ability to increase the likelihood of species coexistence (i.e. biodiversity) on a fragmented landscape controlled by different managers.
An agent-based model to simulate meat consumption behaviour of consumers in Britain
Andrea Scalco | Published Friday, October 18, 2019The current rate of production and consumption of meat poses a problem both to peoples’ health and to the environment. This work aims to develop a simulation of peoples’ meat consumption behaviour in Britain using agent-based modelling. The agents represent individual consumers. The key variables that characterise agents include sex, age, monthly income, perception of the living cost, and concerns about the impact of meat on the environment, health, and animal welfare. A process of peer influence is modelled with respect to the agents’ concerns. Influence spreads across two eating networks (i.e. co-workers and household members) depending on the time of day, day of the week, and agents’ employment status. Data from a representative sample of British consumers is used to empirically ground the model. Different experiments are run simulating interventions of application of social marketing campaigns and a rise in price of meat. The main outcome is the average weekly consumption of meat per consumer. A secondary outcome is the likelihood of eating meat.
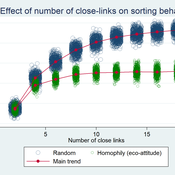
Waste separation in small-world networks
František Kalvas Michaela Kudrnáčová | Published Monday, September 30, 2019The model answers the question how homophily and number of close-links in small-world network influences behavior of consumats. The results show that the more close-links the more probable the consumat follows the major behavior, but homophilly blocks the major behavior and supports survival of the minor behavior.
Homophily as a process generating social networks: insights from Social Distance Attachment model
Szymon Talaga Andrzej Nowak | Published Tuesday, September 17, 2019This is code repository for the paper “Homophily as a process generating social networks: insights from Social Distance Attachment model”.
It provides all information, code and data necessary to replicate all the simulations and analyses presented in the paper.
This document contains the overall instruction as well as description of the content of the repository.
Details regarding particular stages are documented within source files as comments.
NarcoLogic
Nicholas Magliocca | Published Thursday, August 29, 2019Investigate spatial adaptive behaviors of narco-trafficking networks in response to various counterdrug interdiction strategies within the cocaine transit zone of Central America and associated maritime areas. Through the novel application of the ‘complex adaptive systems’ paradigm, we implement a potentially transformative coupled agent-based and interdiction optimization modeling approach to compellingly demonstrate: (a) how current efforts to disrupt narco-trafficking networks are in fact making them more widespread, resilient, and economically powerful; (b) the potential for alternative interdiction approaches to weaken and contain traffickers.
Displaying 10 of 136 results #Networks clear search