About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 70 results climate clear search
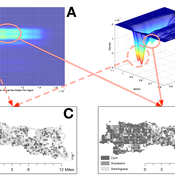
OMOLAND-CA: An Agent-Based Modeling of Rural Households’ Adaptation to Climate Change
Atesmachew Hailegiorgis Andrew Crooks Claudio Cioffi-Revilla | Published Tuesday, July 25, 2017 | Last modified Tuesday, July 10, 2018The purpose of the OMOLAND-CA is to investigate the adaptive capacity of rural households in the South Omo zone of Ethiopia with respect to variation in climate, socioeconomic factors, and land-use at the local level.
Climate Change Adaptation in Coastal Regions
Emma Cutler | Published Thursday, June 01, 2017This generic model simulates climate change adaptation in the form of resistance, accommodation, and retreat in coastal regions vulnerable to sea level rise and flooding. It tracks how population changes as households retreat to higher ground.
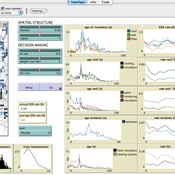
The Groundwater Commons Game
Juan Castilla-Rho Rodrigo Rojas | Published Thursday, May 11, 2017 | Last modified Saturday, September 16, 2017The Groundwater Commons Game synthesises and extends existing work on human cooperation and collective action, to elucidate possible determinants and pathways to regulatory compliance in groundwater systems globally.
Impact of Seasonal Forecast Use on Agricultural Income in a System with Varying Crop Costs and Returns
Thushara Gunda Josh T Bazuin John Nay Kam L Yeung | Published Tuesday, February 07, 2017The objective of the model is to evaluate the impact of seasonal forecasts on a farmer’s net agricultural income when their crop choices have different and variable costs and returns.
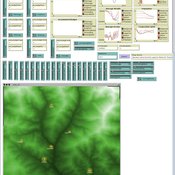
TREELIM
Gudrun Wallentin | Published Wednesday, November 30, 2016 | Last modified Tuesday, January 10, 2017The model simulates the spatial patterns of secondary forest succession above the current alpine tree line in the context of land use and climate change. Three scenarios are offered: (1) climate change, (2) land use change, (3) species composition.
Stylized agricultural land-use model for resilience exploration
Patrick Bitterman | Published Tuesday, June 14, 2016 | Last modified Monday, April 08, 2019This model is a highly stylized land use model in the Clear Creek Watershed in Eastern Iowa, designed to illustrate the construction of stability landscapes within resilience theory.
EmergenceOfClimateMitigation
S Greeven | Published Monday, February 29, 2016A theoretical model of the emergence of climate mitigation - a two-level game theoretic representation
Exploring homeowners' insulation activity
Georg Holtz Emile Chappin Jonas Friege | Published Monday, June 01, 2015 | Last modified Monday, April 08, 2019We built an agent-based model to foster the understanding of homeowners’ insulation activity.
Peer reviewed Simple Coastal Exploitation in the American Samoa
Chloe Atwater | Published Wednesday, November 05, 2014This model employs optimal foraging theory principles to generate predictions of which coastal habitats are exploited in climatically stable versus variable environments, using the American Samoa as a study area.
The model implements a model that reflects features of a rural hill village in Nepal. Key features of the model include water storage, social capital and migration of household members who then send remittances back to the village.
Displaying 10 of 70 results climate clear search