About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 521 results for "Jingjing Cai" clear search
Critical Sustainability Transitions: Relaunching local agriculture after decline (Model code and description)
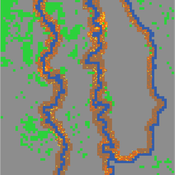
Pedro Lopez-Merino | Published Tuesday, April 30, 2024This model simulates the dynamics of agricultural land use change, specifically the transition between agricultural and non-agricultural land use in a spatial context. It explores the influence of various factors such as agricultural profitability, path dependency, and neighborhood effects on land use decisions.
The model operates on a grid of patches representing land parcels. Each patch can be in one of two states: exploited (green, representing agricultural land) or unexploited (brown, representing non-agricultural land). Agents (patches) transition between these states based on probabilistic rules. The main factors affecting these transitions are agricultural profitability, path dependency, and neighborhood effects.
-Agricultural Profitability: This factor is determined by the prob-agri function, which calculates the probability of a non-agricultural patch converting to agricultural based on income differences between agriculture and other sectors. -Path Dependency: Represented by the path-dependency parameter, it influences the likelihood of patches changing their state based on their current state. It’s a measure of inertia or resistance to change. -Neighborhood Effects: The neighborhood function calculates the number of exploited (agricultural) neighbors of a patch. This influences the decision of a patch to convert to agricultural land, representing the influence of surrounding land use on the decision-making process.
On the liquidity of the illiquid (hard-to-trade) assets
Marcin Czupryna | Published Monday, January 13, 2025This paper investigates the impact of agents' trading decisions on market liquidity and transactional efficiency in markets for illiquid (hard-to-trade) assets. Drawing on a unique order book dataset from the fine wine exchange Liv-ex, we offer novel insights into liquidity dynamics in illiquid markets. Using an agent-based framework, we assess the adequacy of conventional liquidity measures in capturing market liquidity and transactional efficiency. Our main findings reveal that conventional liquidity measures, such as the number of bids, asks, new bids and new asks, may not accurately represent overall transactional efficiency. Instead, volume (measured by the number of trades) and relative spread measures may be more appropriate indicators of liquidity within the context of illiquid markets. Furthermore, our simulations demonstrate that a greater number of traders participating in the market correlates with an increased efficiency in trade execution, while wider trader-set margins may decrease the transactional efficiency. Interestingly, the trading period of the agents appears to have a significant impact on trade execution. This suggests that granting market participants additional time for trading (for example, through the support of automated trading systems) can enhance transactional efficiency within illiquid markets. These insights offer practical implications for market participants and policymakers aiming to optimise market functioning and liquidity.
Peer reviewed E³-MAN. An Institutionally-guided multi-agent. Model for fair and efficient negotiation.
José luis bustelo | Published Monday, September 01, 2025Negotiation plays a fundamental role in shaping human societies, underpinning conflict resolution, institutional design, and economic coordination. This article introduces E³-MAN, a novel multi-agent model for negotiation that integrates individual utility maximization with fairness and institutional legitimacy. Unlike classical approaches grounded solely in game theory, our model incorporates Bayesian opponent modeling, transfer learning from past negotiation domains, and fallback institutional rules to resolve deadlocks. Agents interact in dynamic environments characterized by strategic heterogeneity and asymmetric information, negotiating over multidimensional issues under time constraints. Through extensive simulation experiments, we compare E³-MAN against the Nash bargaining solution and equal-split baselines using key performance metrics: utilitarian efficiency, Nash social welfare, Jain fairness index, Gini coefficient, and institutional compliance. Results show that E³-MAN achieves near-optimal efficiency while significantly improving distributive equity and agreement stability. A legal application simulating multilateral labor arbitration demonstrates that institutional default rules foster more balanced outcomes and increase negotiation success rates from 58% to 98%. By combining computational intelligence with normative constraints, this work contributes to the growing field of socially aware autonomous agents. It offers a virtual laboratory for exploring how simple institutional interventions can enhance justice, cooperation, and robustness in complex socio-legal systems.
Team Structure and Task Performance
Davide Secchi Martin Neumann | Published Monday, August 05, 2024This model was designed to study resilience in organizations. Inspired by ethnographic work, it follows the simple goal to understand whether team structure affects the way in which tasks are performed. In so doing, it compares the ‘hybrid’ data-inspired structure with three more traditional structures (i.e. hierarchy, flexible/relaxed hierarchy, and anarchy/disorganization).
ADAM: Agent-based Demand and Assignment Model
D Levinson | Published Monday, August 29, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The core algorithm is an agent-based model, which simulates travel patterns on a network based on microscopic decision-making by each traveler.
SONG - Simulation of Network Growth
D Levinson | Published Monday, August 29, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013SONG is a simulator designed for simulating the process of transportation network growth.
Model to assess factors that influence local communities compliance with protected areas policies
Gustavo Andrade | Published Monday, November 21, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013We built a model using R,polr package, to assess 55 published case studies from developing countries to determine what factors influence the level of compliance of local communities with protected area regulations.
Peer reviewed Horse population dynamics
Nika Galic | Published Tuesday, November 12, 2013 | Last modified Wednesday, October 29, 2014This model investigates the link between prescribed growth in body size, population dynamics and density dependence through population feedback on available resources.
MERCURY: an ABM of tableware trade in the Roman East
Tom Brughmans Jeroen Poblome | Published Thursday, September 25, 2014 | Last modified Friday, May 01, 2015MERCURY aims to represent and explore two descriptive models of the functioning of the Roman trade system that aim to explain the observed strong differences in the wideness of distributions of Roman tableware.
Peer reviewed Simulating the Economic Impact of Boko Haram on a Cameroonian Floodplain
Mark Moritz Nathaniel Henry Sarah Laborde | Published Saturday, October 22, 2016 | Last modified Wednesday, June 07, 2017This model examines the potential impact of market collapse on the economy and demography of fishing households in the Logone Floodplain, Cameroon.
Displaying 10 of 521 results for "Jingjing Cai" clear search