About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 9 of 39 results us clear search
Peer reviewed Ache hunting
Kim Hill Marco Janssen | Published Tuesday, August 13, 2013 | Last modified Friday, December 21, 2018Agent-based model of hunting behavior of Ache hunter-gatherers from Paraguay. We evaluate the effect of group size and cooperative hunting
A-KinGDom: A Kinship, Grooming and Dominance Model for Primate Societies
Ruth Dolado Francesc S Beltran Vicenc Quera | Published Thursday, July 11, 2013 | Last modified Wednesday, July 17, 2013A-KinGDom simulates the emergence of the social structure in a group of non-human primates. The model includes dominance and affiliative interactions which allow us to define four different attack and affiliative strategies.
Asymmetric two-sided matching
Naoki Shiba | Published Wednesday, January 09, 2013 | Last modified Tuesday, May 28, 2013This model is an extended version of the matching problem including the mate search problem, which is the generalization of a traditional optimization problem. The matching problem is extended to a form of asymmetric two-sided matching problem.
Symmetric two-sided matching
Naoki Shiba | Published Wednesday, January 09, 2013 | Last modified Wednesday, May 29, 2013This is a replication model of the matching problem including the mate search problem, which is the generalization of a traditional optimization problem.
Evolution of indirect reciprocity by social information
Yunhwan Kim | Published Friday, November 02, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Indirect reciprocity can be evolved by the shared information among the people of small subgroups in the population.
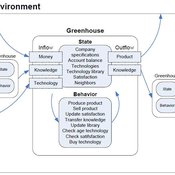
Universal Darwinism in Dutch Greenhouses
Julia Kasmire | Published Wednesday, May 09, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013An ABM, derived from a case study and a series of surveys with greenhouse growers in the Westland, Netherlands. Experiments using this model showshow that the greenhouse horticulture industry displays diversity, adaptive complexity and an uneven distribution, which all suggest that the industry is an evolving system.
Village Ecodynamics Project
ipem | Published Friday, May 13, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The Village Project is designed to help archaeologists understand the factors influencing settlement patterns of small-scale agrarian peoples. Although such societies are becoming increasingly rare, they represent the norm throughout most of the Neolithic period the world over.
John Q. Public (JQP): A Model of Political Judgment and Behavior
Sung-Youn Kim | Published Monday, March 14, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The model integrates major theories of political judgment and behavior within the classical cognitive paradigm embedded in the ACT-R cognitive architecture. It models preferences and beliefs of political candidates, parties, and groups.
Peer reviewed Artificial Anasazi
Marco Janssen | Published Tuesday, September 07, 2010 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Replication of the well known Artificial Anasazi model that simulates the population dynamics between 800 and 1350 in the Long House Valley in Arizona.
Displaying 9 of 39 results us clear search