About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 7 of 37 results spatially explicit clear search
Land Use in the Chitwan Valley
Alex Zvoleff | Published Monday, June 02, 2014chitwanabm is a spatially explicit agent-based model of population and land use in the Chitwan Valley, Nepal, designed to explore feedbacks between population and environment, with a heavy focus on community context and individual-level variation.
Concession Forestry Modeling
Andrew Bell Daniel G Brown Rick L Riolo Jacqueline M Doremus Thomas P Lyon John Vandermeer Arun Agrawal | Published Thursday, January 23, 2014A logging agent builds roads based on the location of high-value hotspots, and cuts trees based on road access. A forest monitor sanctions the logger on observed infractions, reshaping the pattern of road development.
Soil microbe-predator model with enzymes
Randall Boone John C Moore Akihiro Koyama Kirstin Holfelder | Published Thursday, November 21, 2013We seek to improve understanding of roles enzyme play in soil food webs. We created an agent-based simulation of a simple food web that includes enzymatic activity. The model was used in a publication, Moore et al. (in press; Biochemistry).
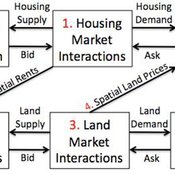
Coupled Housing and Land Markets (CHALMS)
Nicholas Magliocca Virginia Mcconnell Margaret Walls | Published Friday, November 02, 2012 | Last modified Monday, October 27, 2014CHALMS simulates housing and land market interactions between housing consumers, developers, and farmers in a growing ex-urban area.
SimAdapt
François Rebaudo | Published Wednesday, August 29, 2012 | Last modified Monday, October 13, 2014SimAdapt: An individual-based genetic model for simulating landscape management impacts on populations
Alpine land-use allocation model - ALUAM-AB
Simon Briner | Published Tuesday, January 31, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013A model for simulating farmers and foresters response on changing climate and changing socio-economic parameters. Modeled are changes in land-use as well as in ecosystem services provision.
Token Foraging in a Commons Dilemma
Nicholas Radtke | Published Monday, August 31, 2009 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The model aims to mimic the observed behavior of participants in spatially explicit dynamic commons experiments.
Displaying 7 of 37 results spatially explicit clear search