About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 443 results simulation clear search
Kiss Nightclub simulation
Mathieu Bourgais | Published Friday, April 27, 2018 | Last modified Friday, April 05, 2019Model for the simulation of the Kiss Nightclub fevacuations with agents featring cognition, emotions, emotonal contagion, personality, social relations and norms.
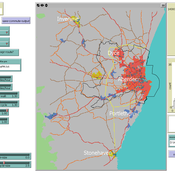
Transport simulation in a real road network
Gary Polhill Jiaqi Ge | Published Tuesday, April 17, 2018 | Last modified Tuesday, April 17, 2018Ge, J., & Polhill, G. (2016). Exploring the Combined Impact of Factors Influencing Commuting Patterns and CO2 Emission in Aberdeen Using an Agent-Based Model. Journal of Artificial Societies and Social Simulation, 19(3). http://jasss.soc.surrey.ac.uk/19/3/11.html
We develop an agent-based transport model using a realistic GIS-enabled road network and the car following method. The model can be used to study the impact of social interventions such as flexi-time and workplace sharing, as well as large infrastructure such as the construction of a bypass or highway. The model is developed in Netlogo version 5 and requires road network data in GIS format to run.
Stoplight parrotfish population model
Tyler Pavlowich | Published Monday, April 02, 2018This agent-based model simulates a stoplight parrotfish population in a heavily-fished Caribbean coral reef. The model allows for the simulation of various fishing regulations and observation of population and catch outcomes. It was built using the structure and equations from several previously published models, including the work of Bozec et al. (2016) and Alonzo and Mangel (2004 and 2005). The initial model conditions are parameterized to population and fishing data collected in Buen Hombre, Dominican Republic by Tyler Pavlowich.
High Standards Enhance Inequality in Idealized Labor Markets
Károly Takács | Published Tuesday, March 20, 2018Takács, K. and Squazzoni, F. 2015. High Standards Enhance Inequality in Idealized Labor Markets. Journal of Artificial Societies and Social Simulation, 18(4), 2, http://jasss.soc.surrey.ac.uk/18/4/2.html
We built a simple model of an idealized labor market, in which there is no objective difference in average quality between groups and hiring decisions are not biased in favor of any particular group. Our results show that inequality in employment emerges necessarily also in such idealized situations due to the limited supply of high quality individuals and asymmetric information. Inequalities are exacerbated when employers have high standards and keep only the best workers in house. We found that ambitious workers get higher quality jobs even if ambition does not correlate or even negatively correlates with internal quality. Our findings help to corroborate empirical findings on higher employment discrepancies in high rather than low status jobs.
DiDIY Factory
Ruth Meyer | Published Tuesday, February 20, 2018The DiDIY-Factory model is a model of an abstract factory. Its purpose is to investigate the impact Digital Do-It-Yourself (DiDIY) could have on the domain of work and organisation.
DiDIY can be defined as the set of all manufacturing activities (and mindsets) that are made possible by digital technologies. The availability and ease of use of digital technologies together with easily accessible shared knowledge may allow anyone to carry out activities that were previously only performed by experts and professionals. In the context of work and organisations, the DiDIY effect shakes organisational roles by such disintermediation of experts. It allows workers to overcome the traditionally strict organisational hierarchies by having direct access to relevant information, e.g. the status of machines via real-time information systems implemented in the factory.
A simulation model of this general scenario needs to represent a more or less abstract manufacturing firm with supervisors, workers, machines and tasks to be performed. Experiments with such a model can then be run to investigate the organisational structure –- changing from a strict hierarchy to a self-organised, seemingly anarchic organisation.
Peer reviewed Population Genetics
Kristin Crouse | Published Thursday, February 08, 2018 | Last modified Wednesday, September 09, 2020This model simulates the mechanisms of evolution, or how allele frequencies change in a population over time.
Agent-based model for the socio-economic monitoring of visitor streams
Stefan Mohr | Published Saturday, January 20, 2018Due to the large extent of the Harz National Park, an accurate measurement of visitor numbers and their spatiotemporal distribution is not feasible. This model demonstrates the possibility to simulate the streams of visitors with ABM methodology.
Generalized Trust in the Mirror - a model on the Dynamics of Trust
Dominik Klein Johannes Marx | Published Friday, January 12, 2018This model studies the emergence and dynamics of generalized trust. It does so by modeling agents that engage in trust games and, based on their experience, slowly determine whether others are, in general, trustworthy.
Simulation of the Governance of Complex Systems
Fabian Adelt Johannes Weyer Robin D Fink Andreas Ihrig | Published Monday, December 18, 2017 | Last modified Friday, March 02, 2018Simulation-Framework to study the governance of complex, network-like sociotechnical systems by means of ABM. Agents’ behaviour is based on a sociological model of action. A set of basic governance mechanisms helps to conduct first experiments.
HMODEL: an exploratory simulation of surface archaeological formation
Benjamin Davies Simon Holdaway Patricia Fanning | Published Thursday, November 30, 2017This model is used to simulate the influence of spatially and temporally variable sedimentary processes on the distribution of dated archaeological features in a surface context.
Displaying 10 of 443 results simulation clear search