About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 30 results trust clear search
Peer reviewed Zimbabwe Agro-Pastoral Management Model (ZAPMM): Musimboti wevanhu, zvipfuo nezvirimwa
MV Eitzel Solera Kleber Tulio Neves Jon Solera Kenneth B Wilson Abraham Mawere Ndlovu Aaron C Fisher André Veski Oluwasola E Omoju Emmanuel Mhike Hove | Published Tuesday, June 19, 2018This model has been created with and for the researcher-farmers of the Muonde Trust (http://www.muonde.org/), a registered Zimbabwean non-governmental organization dedicated to fostering indigenous innovation. Model behaviors and parameters (mashandiro nemisiyano nedzimwe model) derive from a combination of literature review and the collected datasets from Muonde’s long-term (over 30 years) community-based research. The goals of this model are three-fold (muzvikamu zvitatu):
A) To represent three components of a Zimbabwean agro-pastoral system (crops, woodland grazing area, and livestock) along with their key interactions and feedbacks and some of the human management decisions that may affect these components and their interactions.
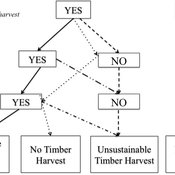
B) To assess how climate variation (implemented in several different ways) and human management may affect the sustainability of the system as measured by the continued provisioning of crops, livestock, and woodland grazing area.
C) To provide a discussion tool for the community and local leaders to explore different management strategies for the agro-pastoral system (hwaro/nzira yekudyidzana kwavanhu, zvipfuo nezvirimwa), particularly in the face of climate change.
Generalized Trust in the Mirror - a model on the Dynamics of Trust
Dominik Klein Johannes Marx | Published Friday, January 12, 2018This model studies the emergence and dynamics of generalized trust. It does so by modeling agents that engage in trust games and, based on their experience, slowly determine whether others are, in general, trustworthy.
SMILI-T: Small-scale fisheries institutions and local interactions for transformations
Emilie Lindkvist Maja Schlüter Xavier Basurto | Published Tuesday, January 09, 2018 | Last modified Friday, March 26, 2021This model examines how financial and social top-down interventions interplay with the internal self-organizing dynamics of a fishing community. The aim is to transform from hierarchical fishbuyer-fisher relationship into fishing cooperatives.
Modeling a Victim-Centered Approach for Detection of Human Trafficking Victims within Migration Flows
Kyle Ballard Brant M Horio | Published Saturday, September 23, 2017The model employs an agent-based model for exploring the victim-centered approach to identifying human trafficking and the approach’s effectiveness in an abstract representation of migrant flows.
Sorghum supply development in Meru County, Kenya
Tim Verwaart Coen Van Wagenberg | Published Wednesday, September 06, 2017 | Last modified Thursday, May 30, 2019Trust between farmers and processors is a key factor in developing stable supply chains including “bottom of the pyramid”, small-scale farmers. This simulation studies a case with 10000 farmers.
Expectation-Based Bayesian Belief Revision
C Merdes Momme Von Sydow Ulrike Hahn | Published Monday, June 19, 2017 | Last modified Monday, August 06, 2018This model implements a Bayesian belief revision model that contrasts an ideal agent in possesion of true likelihoods, an agent using a fixed estimate of trusting its source of information, and an agent updating its trust estimate.
SMILI: Small-scale fisheries Institutions and Local Interactions
Emilie Lindkvist Maja Schlüter Xavier Basurto | Published Thursday, March 09, 2017The model represents an archetypical fishery in a co-evolutionary social-ecological environment, capturing different dimensions of trust between fishers and fish buyers for the establishment and persistence of self-governance arrangements.
Private forest owner management behavior using social interactions, information flow, and peer-to-peer n
Jessica Leahy Emily Silver Huff Aaron R Weiskittel Caroline L Noblet David Hiebeler | Published Tuesday, October 13, 2015This theoretical model includes forested polygons and three types of agents: forest landowners, foresters, and peer leaders. Agent rules and characteristics were parameterized from existing literature and an empirical survey of forest landowners.
REHAB: A Role Playing Game to Explore the Influence of Knowledge and Communication on Natural Resources Management
Christophe Le Page Anne Dray Pascal Perez Claude Garcia | Published Monday, July 13, 2015 | Last modified Monday, July 13, 2015REHAB has been designed as an ice-breaker in courses dealing with ecosystem management and participatory modelling. It helps introducing the two main tools used by the Companion Modelling approach, namely role-playing games and agent-based models.
This is a social trust model for investigating the social relationships and social networks in the real world and in social media.
Displaying 10 of 30 results trust clear search