About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 443 results simulation clear search
EMMIT (Extendable Model for Malaria Intervention Testing)
Jacob Heintzelman Greg R Madey | Published Thursday, May 27, 2021EMMIT is an end-user developed agent-based simulation of malaria transmission. The simulation’s development is a case study demonstrating an approach for non-technical investigators to easily develop useful simulations of complex public health problems. We focused on malaria transmission, a major global public health problem, and insecticide resistance (IR), a major problem affecting malaria control. Insecticides are used to reduce transmission of malaria caused by the Plasmodium parasite that is spread by the Anopheles mosquito. However, the emergence and spread of IR in a mosquito population can diminish the insecticide’s effectiveness. IR results from mutations that produce behavioral changes or biochemical changes (such as detoxification enhancement, target site alterations) in the mosquito population that provide resistance to the insecticide. Evolutionary selection for the IR traits reduces the effectiveness of an insecticide favoring the resistant mosquito population. It has been suggested that biopesticides, and specifically those that are Late Life Acting (LLA), could address this problem. LLA insecticides exploit Plasmodium’s approximate 10-day extrinsic incubation period in the mosquito vector, a delay that limits malaria transmission to older infected mosquitoes. Since the proposed LLA insecticide delays mosquito death until after the exposed mosquito has a chance to produce several broods of offspring, reducing the selective pressure for resistance, it delays IR development and gives the insecticide longer effectivity. Such insecticides are designed to slow the evolution of IR thus maintaining their effectiveness for malaria control. For the IR problem, EMMIT shows that an LLA insecticide could work as intended, but its operational characteristics are critical, primarily the mean-time-to-death after exposure and the associated standard deviation. We also demonstrate the simulation’s extensibility to other malaria control measures, including larval source control and policies to mitigate the spread of IR. The simulation was developed using NetLogo as a case study of a simple but useful approach to public health research.
Open Peer Review Model
Federico Bianchi | Published Monday, May 24, 2021This is an agent-based model of a population of scientists alternatively authoring or reviewing manuscripts submitted to a scholarly journal for peer review. Peer-review evaluation can be either ‘confidential’, i.e. the identity of authors and reviewers is not disclosed, or ‘open’, i.e. authors’ identity is disclosed to reviewers. The quality of the submitted manuscripts vary according to their authors’ resources, which vary according to the number of publications. Reviewers can assess the assigned manuscript’s quality either reliably of unreliably according to varying behavioural assumptions, i.e. direct/indirect reciprocation of past outcome as authors, or deference towards higher-status authors.
Team Cognition
Iris Lorscheid | Published Sunday, May 23, 2021The teamCognition model investigates team decision processes by using an agent-based model to conceptualize team decisions as an emergent property. It uses a mixed-method research design with a laboratory experiment providing qualitative and quantitative input for the model’s construction, as well as data for an output validation of the model. The agent-based model is used as a computational testbed to contrast several processes of team decision making, representing potential, simplified mechanisms of how a team decision emerges. The increasing overall fit of the simulation and empirical results indicates that the modeled decision processes can at least partly explain the observed team decisions.
Peer reviewed A Macroeconomic Model of a Closed Economy
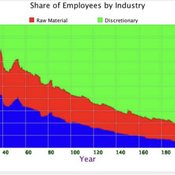
Ian Stuart | Published Saturday, May 08, 2021 | Last modified Wednesday, June 23, 2021This model/program presents a “three industry model” that may be particularly useful for macroeconomic simulations. The main purpose of this program is to demonstrate a mechanism in which the relative share of labor shifts between industries.
Care has been taken so that it is written in a self-documenting way so that it may be useful to anyone that might build from it or use it as an example.
This model is not intended to match a specific economy (and is not calibrated to do so) but its particular minimalist implementation may be useful for future research/development.
…
Peer reviewed Are Countertrade credits as flexible and efficient as cash? A novel approach to reducing income inequality using countertrade methodology.
Peter Malliaros | Published Monday, May 03, 2021 | Last modified Tuesday, May 11, 2021The impacts of income inequality can be seen everywhere, regardless of the country or the level of economic development. According to the literature review, income inequality has negative impacts in economic, social, and political variables. Notwithstanding of how well or not countries have done in reducing income inequality, none have been able to reduce it to a Gini Coefficient level of 0.2 or less.
This is the promise that a novel approach called Counterbalance Economics (CBE) provides without the need of increased taxes.
Based on the simulation, introducing the CBE into the Australian, UK, US, Swiss or German economies would result in an overall GDP increase of under 1% however, the level of inequality would be reduced from an average of 0.33 down to an average of 0.08. A detailed explanation of how to use the model, software, and data dependencies along with all other requirements have been included as part of the info tab in the model.
Simulation model replicating the five different games that were run during a workshop of the TISSS Lab
tissslab | Published Friday, April 30, 2021The three-day participatory workshop organized by the TISSS Lab had 20 participants who were academics in different career stages ranging from university student to professor. For each of the five games, the participants had to move between tables according to some pre-specified rules. After the workshop both the participant’s perception of the games’ complexities and the participants’ satisfaction with the games were recorded.
In order to obtain additional objective measures for the games’ complexities, these games were also simulated using this simulation model here. Therefore, the simulation model is an as-accurate-as-possible reproduction of the workshop games: it has 20 participants moving between 5 different tables. The rules that specify who moves when vary from game to game. Just to get an idea, Game 3 has the rule: “move if you’re sitting next to someone who is waring white or no socks”.
An exact description of the workshop games and the associated simulation models can be found in the paper “The relation between perceived complexity and happiness with decision situations: searching for objective measures in social simulation games”.
This model presents an autonomous, two-lane driving environment with a single lane-closure that can be toggled. The four driving scenarios - two baseline cases (based on the real-world) and two experimental setups - are as follows:
- Baseline-1 is where cars are not informed of the lane closure.
- Baseline-2 is where a Red Zone is marked wherein cars are informed of the lane closure ahead.
- Strategy-1 is where cars use a co-operative driving strategy - FAS. <sup>[1]</sup>
- Strategy-2 is a variant of Strategy-1 and uses comfortable deceleration values instead of the vehicle’s limit.
…
AIforGoodSimulator - Modeling Covid-19 Spread and Potential Interventions in Refugee Camps
Shyaam Ramkumar Woi Sok Oh | Published Thursday, March 18, 2021The Netlogo model is a conceptualization of the Moria refugee camp, capturing the household demographics of refugees in the camp, a theoretical friendship network based on values, and an abstraction of their daily activities. The model then simulates how Covid-19 could spread through the camp if one refugee is exposed to the virus, utilizing transmission probabilities and the stages of disease progression of Covid-19 from susceptible to exposed to asymptomatic / symptomatic to mild / severe to recovered from literature. The model also incorporates various interventions - PPE, lockdown, isolation of symptomatic refugees - to analyze how they could mitigate the spread of the virus through the camp.
The Effect of Individual and Collective Characteristics on Team Performance: A Model of Networked Agents Engaged in Collective Problem Solving
Amin Boroomand | Published Tuesday, March 16, 2021 | Last modified Monday, July 26, 2021This code is for an agent-based model of collective problem solving in which agents with different behavior strategies, explore the NK landscape while they communicate with their peers agents. This model is based on the famous work of Lazer, D., & Friedman, A. (2007), The network structure of exploration and exploitation.
A data-informed bounded-confidence opinion dynamics model
Bruce Edmonds | Published Wednesday, March 10, 2021The simulation is a variant of the “ToRealSim OD variants - base v2.7” base model, which is based on the standard DW opinion dynamics model (but with the differences that rather than one agent per tick randomly influencing another, all agents randomly influence one other per tick - this seems to make no difference to the outcomes other than to scale simulation time). Influence can be made one-way by turning off the two-way? switch
Various additional variations and sources of noise are possible to test robustness of outcomes to these (compared to DW model).
In this version agent opinions change following the empirical data collected in some experiments (Takács et al 2016).
Such an algorithm leaves no role for the uncertainties in other OD models. [Indeed the data from (Takács et al 2016) indicates that there can be influence even when opinion differences are large - which violates a core assumption of these]. However to allow better comparison with other such models there is a with-un? switch which allows uncertainties to come into play. If this is on, then influence (according to above algorithm) is only calculated if the opinion difference is less than the uncertainty. If an agent is influenced uncertainties are modified in the same way as standard DW models.
Displaying 10 of 443 results simulation clear search