About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 152 results making clear search
Irrigation game
Marco Janssen | Published Monday, July 23, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Irrigation game calibrated on experimental data
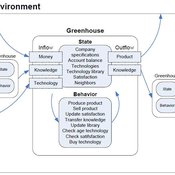
Universal Darwinism in Dutch Greenhouses
Julia Kasmire | Published Wednesday, May 09, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013An ABM, derived from a case study and a series of surveys with greenhouse growers in the Westland, Netherlands. Experiments using this model showshow that the greenhouse horticulture industry displays diversity, adaptive complexity and an uneven distribution, which all suggest that the industry is an evolving system.
Collective Decision Making for Ecological Restoration
Dean Massey Moira Zellner Cristy Watkins Jeremy Brooks Kristen Ross | Published Friday, December 30, 2011 | Last modified Friday, November 21, 2014We present an agent-based model that maps out and simulates the processes by which individuals within ecological restoration organizations communicate and collectively make restoration decisions.
Agent-based model of sexual partnership
Andrea Knittel | Published Monday, December 05, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013In this model agents meet, evaluate one another, decide whether or not to date, if and when to become sexual partners, and when to break up.
Diffusion dynamics in small-world networks with heterogeneous consumers
Sebastiano Delre | Published Saturday, September 10, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This model simulates diffusion curves and it allows to test how social influence, network structure and consumer heterogeneity affect their spreads and their speeds.
SONG - Simulation of Network Growth
D Levinson | Published Monday, August 29, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013SONG is a simulator designed for simulating the process of transportation network growth.
ADAM: Agent-based Demand and Assignment Model
D Levinson | Published Monday, August 29, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The core algorithm is an agent-based model, which simulates travel patterns on a network based on microscopic decision-making by each traveler.
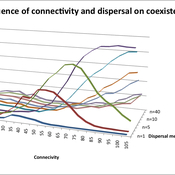
Varying effects of connectivity and dispersal on interacting species dynamics
Kehinde Salau | Published Monday, August 29, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013An agent-based model of species interaction on fragmented landscape is developed to address the question, how do population levels of predators and prey react with respect to changes in the patch connectivity as well as changes in the sharpness of threshold dispersal?
An empirical ABM for regional land use/cover change: a Dutch case study
Diego Valbuena | Published Saturday, March 12, 2011 | Last modified Thursday, November 11, 2021This is an empirical model described in http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2010.05.001. The objective of the model is to simulate how the decision-making of farmers/agents with different strategies can affect the landscape structure in a region in the Netherlands.
Primate Group Decision Making
j.zappala | Published Wednesday, August 11, 2010 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This model contains source code and a technical appendix for the paper “Effects of Resource Availability on Consensus Decision Making in Primates”.
Displaying 10 of 152 results making clear search