About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1259 results
SEDIBASES
Sebastian Rasch | Published Monday, October 20, 2014The Sediba socio-ecolgoical rangeland model is an biomass growth model coupled with a social model of pastoralist behaviour in a commmon pool resource setting. The social subsystem is an empircal ABM.
A minimal assumption based agent based simulation model of the emergence of technological innovation
Yuan Zhao Roland Ortt Bernhard Katzy | Published Sunday, October 19, 2014This simulation model is to simulate the emergence of technological innovation processes from the hypercycles perspective.
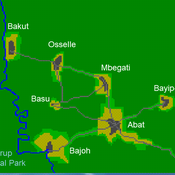
A stylized scale model to codesign with villagers an agent-based model of bushmeat hunting in the periphery of Korup National Park (Cameroon)
A Complex Model of Voter Turnout
Bruce Edmonds Laurence Lessard-Phillips Ed Fieldhouse | Published Monday, October 13, 2014 | Last modified Tuesday, August 18, 2015This is a complex “Data Integration Model”, following a “KIDS” rather than a “KISS” methodology - guided by the available evidence. It looks at the complex mix of social processes that may determine why people vote or not.
Wave When the Hale Wale (WWHW)
María Pereda José Manuel Galán Iván Briz I Godino Jorge Caro Débora Zurro Myriam Álvarez José Santos | Published Friday, October 10, 2014 | Last modified Wednesday, April 25, 2018WWHW is an agent-based model designed to allow the exploration of the emergence, resilience and evolution of cooperative behaviours in hunter-fisher-gatherer societies.
Infantry Company Engagement Model with Command and Control
Woo-Seop Yun | Published Monday, October 06, 2014 | Last modified Monday, April 08, 2019Infantry Company Engagement model including command and control functions for the scenario of an offensive operation of the blue force
Simulation model for compliance behaviour
Esther Van Asselt Sjoukje A Osinga | Published Friday, October 03, 2014 | Last modified Tuesday, December 08, 2015This model can be used to optimize intervention strategies for inspection services.
MERCURY: an ABM of tableware trade in the Roman East
Tom Brughmans Jeroen Poblome | Published Thursday, September 25, 2014 | Last modified Friday, May 01, 2015MERCURY aims to represent and explore two descriptive models of the functioning of the Roman trade system that aim to explain the observed strong differences in the wideness of distributions of Roman tableware.
Emerging innovation niches model
Antonio Lopolito Richard Taylor Piergiuseppe Morone | Published Monday, September 22, 2014Objective of our model is to simulate the emergence and operation of a technological niches (TN) in terms of actors’ interaction. A TN can be conceived as protected socio-economic space where radical innovations are developed and tested
Formation of Lithic Assemblages v. 1
C Michael Barton Julien Riel-Salvatore | Published Thursday, September 04, 2014This model represents technological and ecological behaviors of mobile hunter-gatherers, in a variable environment, as they produce, use, and discard chipped stone artifacts. The results can be analyzed and compared with archaeological sites.
Displaying 10 of 1259 results