About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers at all levels engage in the establishment and adoption of community standards and good practices for developing and sharing computational models. Model authors can freely publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library alongside narrative documentation, open science metadata, and other emerging open science norms that facilitate software citation, reproducibility, interoperability, and reuse. Model authors can also request peer review of their computational models to receive a DOI.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with additional detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 134 results environment clear
This is the R code of the mathematical model that includes the decision making formulations for artificial agents. Plus, the code for graphical output is also added to the original code.
Village Ecodynamics Project
ipem | Published Friday, May 13, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The Village Project is designed to help archaeologists understand the factors influencing settlement patterns of small-scale agrarian peoples. Although such societies are becoming increasingly rare, they represent the norm throughout most of the Neolithic period the world over.
Influence with over-confident agents
Juliette Rouchier Emily Tanimura | Published Wednesday, October 21, 2015Agents can influence each other if they are close enough in knowledge. The probability to convince with good knowledge and number of agents have an impact on the dissemination of knowledge.
The Pampas Model: An agent-based model of agricultural systems in the Argentinean Pampas
Federico Bert Guillermo P Podestá Santiago L Rovere Michael North Charles Macal | Published Tuesday, July 16, 2013 | Last modified Tuesday, February 17, 2015The Pampas Model is an Agent-Based Model intended to explore the dynamics of structural and land use changes in agricultural systems of the Argentine Pampas in response to climatic, technological economic, and political drivers.
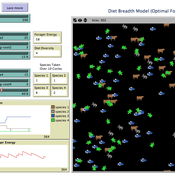
Diet breadth model from Optimal Foraging Theory (Human Behavioral Ecology)
C Michael Barton | Published Wednesday, November 26, 2008 | Last modified Thursday, March 12, 2015Diet breadth is a classic optimal foraging theory (OFT) model from human behavioral ecology (HBE). Different resources, ranked according to their food value and processing costs, are distributed in th
Setting the Stage for Inequality
Timothy Dennehy | Published Monday, March 11, 2013 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013How can a strictly egalitarian social system give way to a stratified society if all of its members punish each other for any type of selfish behavior? This model examines the role of prestige bias in constant and variable environments on the development of hierarchies of wealth.
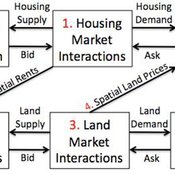
Coupled Housing and Land Markets (CHALMS)
Nicholas Magliocca Virginia Mcconnell Margaret Walls | Published Friday, November 02, 2012 | Last modified Monday, October 27, 2014CHALMS simulates housing and land market interactions between housing consumers, developers, and farmers in a growing ex-urban area.
Exploring social psychology theory for modelling farmer decision-making
James Millington | Published Tuesday, September 18, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013To investigate the potential of using Social Psychology Theory in ABMs of natural resource use and show proof of concept, we present an exemplary agent-based modelling framework that explicitly represents multiple and hierarchical agent self-concepts
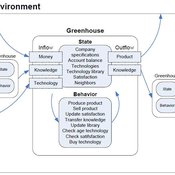
Universal Darwinism in Dutch Greenhouses
Julia Kasmire | Published Wednesday, May 09, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013An ABM, derived from a case study and a series of surveys with greenhouse growers in the Westland, Netherlands. Experiments using this model showshow that the greenhouse horticulture industry displays diversity, adaptive complexity and an uneven distribution, which all suggest that the industry is an evolving system.
The various technologies used inside a Dutch greenhouse interact in combination with an external climate, resulting in an emergent internal climate, which contributes to the final productivity of the greenhouse. This model examines how differing technology development styles affects the overall ability of a community of growers to approach the theoretical maximum yield.
Displaying 10 of 134 results environment clear