About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers at all levels engage in the establishment and adoption of community standards and good practices for developing and sharing computational models. Model authors can freely publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library alongside narrative documentation, open science metadata, and other emerging open science norms that facilitate software citation, reproducibility, interoperability, and reuse. Model authors can also request peer review of their computational models to receive a DOI.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with additional detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 158 results for 'M Vavier'
Managing networked landscapes: conservation in fragmented, regionally connected world
Jacopo Baggio Michael Schoon Sechindra Vallury | Published Monday, December 09, 2019Exploring how learning and social-ecological networks influence management choice set and their ability to increase the likelihood of species coexistence (i.e. biodiversity) on a fragmented landscape controlled by different managers.
A network agent-based model of ethnocentrism and intergroup cooperation
Ross Gore | Published Sunday, October 27, 2019We present a network agent-based model of ethnocentrism and intergroup cooperation in which agents from two groups (majority and minority) change their communality (feeling of group solidarity), cooperation strategy and social ties, depending on a barrier of “likeness” (affinity). Our purpose was to study the model’s capability for describing how the mechanisms of preexisting markers (or “tags”) that can work as cues for inducing in-group bias, imitation, and reaction to non-cooperating agents, lead to ethnocentrism or intergroup cooperation and influence the formation of the network of mixed ties between agents of different groups. We explored the model’s behavior via four experiments in which we studied the combined effects of “likeness,” relative size of the minority group, degree of connectivity of the social network, game difficulty (strength) and relative frequencies of strategy revision and structural adaptation. The parameters that have a stronger influence on the emerging dominant strategies and the formation of mixed ties in the social network are the group-tag barrier, the frequency with which agents react to adverse partners, and the game difficulty. The relative size of the minority group also plays a role in increasing the percentage of mixed ties in the social network. This is consistent with the intergroup ties being dependent on the “arena” of contact (with progressively stronger barriers from e.g. workmates to close relatives), and with measures that hinder intergroup contact also hindering mutual cooperation.
Peer reviewed The foraging potential of the Holocene Cape South Coast of South Africa without the Palaeo-Agulhas Plain
Colin Wren Marco Janssen | Published Monday, August 12, 2019The Palaeo-Agulhas Plain formed an important habitat exploited by Pleistocene hunter-gatherer populations during periods of lower sea level. This productive, grassy habitat would have supported numerous large-bodied ungulates accessible to a population of skilled hunters with the right hunting technology. It also provided a potentially rich location for plant food collection, and along its shores a coastline that moved with the rise and fall of sea levels. The rich archaeological and paleontological records of Pleistocene sites along the modern Cape south coast of South Africa, which would have overlooked the Palaeo-Agulhas Plain during Pleistocene times of lower sea level, provides a paleoarchive of this extinct ecosystem. In this paper, we present a first order illustration of the “palaeoscape modeling” approach advocated by Marean et al. (2015). We use a resourcescape model created from modern studies of habitat productivity without the Palaeo-Agulhas Plain. This is equivalent to predominant Holocene conditions. We then run an agent-based model of the human foraging system to investigate several research questions. Our agent-based approach uses the theoretical framework of optimal foraging theory to model human foraging decisions designed to optimize the net caloric gains within a complex landscape of spatially and temporally variable resources. We find that during the high sea-levels of MIS 5e (+5-6 m asl) and the Holocene, the absence of the Plain left a relatively poor food base supporting a much smaller population relying heavily on edible plant resources from the current Cape flora. Despite high species diversity of plants with edible storage organs, and marine invertebrates, encounter rates with highly profitable resources were low. We demonstrate that without the Palaeo-Agulhas Plain, human populations must have been small and low density, and exploited plant, mammal, and marine resources with relatively low caloric returns. The exposure and contraction of the Palaeo-Agulhas Plain was likely the single biggest driver of behavioral change during periods of climate change through the Pleistocene and into the transition to the Holocene.
Peer reviewed Garbage can model Excel reconstruction
Smarzhevskiy Ivan | Published Tuesday, August 19, 2014 | Last modified Tuesday, July 30, 2019Reconstruction of the original code M. Cohen, J. March, and J. Olsen garbage can model, realized by means of Microsoft Office Excel 2010
Individual bias and organizational objectivity
Bo Xu | Published Monday, April 15, 2013 | Last modified Monday, April 08, 2019This model introduces individual bias to the model of exploration and exploitation, simulates knowledge diffusion within organizations, aiming to investigate the effect of individual bias and other related factors on organizational objectivity.
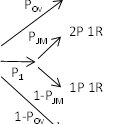
Sunshine or Shield?: Secret Voting Procedures and Legislative Accountability
Michele Buttò Carlos Pereira Matthew Taylor | Published Tuesday, June 24, 2014 | Last modified Monday, April 08, 2019An agent-based model is used to simulate legislators’ behavior under secret voting rules, as influenced by the power of the accused politician, the composition of the voting body, and the publicity of the accusations.
Bicycle encounter model
Gudrun Wallentin | Published Saturday, October 29, 2016 | Last modified Friday, March 29, 2019This Bicycle encounter model builds on the Salzburg Bicycle model (Wallentin & Loidl, 2015). It simulates cyclist flows and encounters, which are locations of potential accidents between cyclists.
Imperfect knowledge and stable governance in democracies
Carlos Fernández-Márquez Francisco Jose Vazquez Luis Fernando Medina | Published Tuesday, February 05, 2019In this paper we introduce an agent-based model of elections and government formation where voters do not have perfect knowledge about the parties’ ideological position. Although voters are boundedly rational, they are forward-looking in that they try to assess the likely impact of the different parties over the resulting government. Thus, their decision rules combine sincere and strategic voting: they form preferences about the different parties but deem some of them as inadmissible and try to block them from office. We find that the most stable and durable coalition governments emerge at intermediate levels of informational ambiguity. When voters have very poor information about the parties, their votes are scattered too widely, preventing the emergence of robust majorities. But also, voters with highly precise perceptions about the parties will cluster around tiny electoral niches with a similar aggregate effect.
A simple emulation-based computational model
Carlos Fernández-Márquez Francisco J Vázquez | Published Tuesday, May 21, 2013 | Last modified Tuesday, February 05, 2019Emulation is one of the simplest and most common mechanisms of social interaction. In this paper we introduce a descriptive computational model that attempts to capture the underlying dynamics of social processes led by emulation.
Online Collaboration, Competing for Attention
Miles Manning | Published Wednesday, July 19, 2017 | Last modified Thursday, January 24, 2019This is a model of a community of online communities. Using mechanisms such as win-stay, lose-shift, and preferential attachment the model can reproduce similar patterns to those of the Stack Exchange network.
Displaying 10 of 158 results for 'M Vavier'