About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 88 results scale clear search
Relative Agreement Model and Network Structure
Spiro Maroulis David Adelberg | Published Friday, January 29, 2016This adaptation of the Relative Agreement model of opinion dynamics (Deffuant et al. 2002) extends the Meadows and Cliff (2012) implementation of this model in a manner that explores the effect of the network structure among the agents.
Micro-level Adaptation, Macro-level Selection, and the Dynamics of Market Partitioning
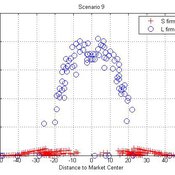
César García-Díaz | Published Monday, October 19, 2015 | Last modified Monday, October 19, 2015This model simulates the emergence of a dual market structure from firm-level interaction. Firms are profit-seeking, and demand is represented by a unimodal distribution of consumers along a set of taste positions.
Peer reviewed Hohokam Trade Networks Model
Joshua Watts | Published Sunday, October 26, 2014The Hohokam Trade Networks Model focuses on key features of the Hohokam economy to explore how differences in trade network topologies may show up in the archaeological record. The model is set in the Phoenix Basin of central Arizona, AD 200-1450.
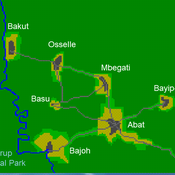
A stylized scale model to codesign with villagers an agent-based model of bushmeat hunting in the periphery of Korup National Park (Cameroon)
The role of spatial foresight in models of hominin dispersal
Colin Wren | Published Monday, February 24, 2014 | Last modified Monday, July 14, 2014The natural selection of foresight, an accuracy at assess the environment, under degrees of environmental heterogeneity. The model is designed to connect local scale mobility, from foraging, with the global scale phenomenon of population dispersal.
The purpose of the AdaptPumpa model is to analyze the robustness of the Pumpa irrigation system in Nepal to climate change.
Informal Information Transmission Networks among Medieval Genoese Investors
Christopher Frantz | Published Wednesday, October 09, 2013 | Last modified Thursday, October 24, 2013This model represents informal information transmission networks among medieval Genoese investors used to inform each other about cheating merchants they employed as part of long-distance trade operations.
01a ModEco V2.05 – Model Economies – In C++
Garvin Boyle | Published Monday, February 04, 2013 | Last modified Friday, April 14, 2017Perpetual Motion Machine - A simple economy that operates at both a biophysical and economic level, and is sustainable. The goal: to determine the necessary and sufficient conditions of sustainability, and the attendant necessary trade-offs.
Peer reviewed Pumpa irrigation model
Marco Janssen Irene Perez Ibarra | Published Wednesday, January 09, 2013 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This is a replication of the Pumpa model that simulates the Pumpa Irrigation System in Nepal (Cifdaloz et al., 2010).
Enhancing recycling of construction materials; an agent based model with empirically based decision parameters
Igor Nikolic Claudia Binder Christof Knoeri Hans-Joerg Althaus | Published Sunday, October 21, 2012 | Last modified Monday, June 09, 2014This model allows for analyzing the most efficient levers for enhancing the use of recycled construction materials, and the role of empirically based decision parameters.
Displaying 10 of 88 results scale clear search