About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 9 of 59 results Farmers clear search
01a ModEco V2.05 – Model Economies – In C++
Garvin Boyle | Published Monday, February 04, 2013 | Last modified Friday, April 14, 2017Perpetual Motion Machine - A simple economy that operates at both a biophysical and economic level, and is sustainable. The goal: to determine the necessary and sufficient conditions of sustainability, and the attendant necessary trade-offs.
Exploring social psychology theory for modelling farmer decision-making
James Millington | Published Tuesday, September 18, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013To investigate the potential of using Social Psychology Theory in ABMs of natural resource use and show proof of concept, we present an exemplary agent-based modelling framework that explicitly represents multiple and hierarchical agent self-concepts
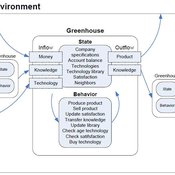
Universal Darwinism in Dutch Greenhouses
Julia Kasmire | Published Wednesday, May 09, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013An ABM, derived from a case study and a series of surveys with greenhouse growers in the Westland, Netherlands. Experiments using this model showshow that the greenhouse horticulture industry displays diversity, adaptive complexity and an uneven distribution, which all suggest that the industry is an evolving system.
Alpine land-use allocation model - ALUAM-AB
Simon Briner | Published Tuesday, January 31, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013A model for simulating farmers and foresters response on changing climate and changing socio-economic parameters. Modeled are changes in land-use as well as in ecosystem services provision.
A model of groundwater usage by farmers in the Upper Guadiana, Spain
Georg Holtz | Published Thursday, June 30, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013An agent-based model to investigate the history of irrigated agriculture in the Upper Guadiana Basin, Spain, in order to learn about the influence of farmers’ characteristics (inter alia profit orientation, risk aversion, skills, available labour force and farm size) on land-use change and associated groundwater over-use in this region.
A Multi-Agent Simulation Approach to Farmland Auction Markets
James Nolan | Published Wednesday, June 22, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This model explores the effects of agent interaction, information feedback, and adaptive learning in repeated auctions for farmland. It gathers information for three types of sealed-bid auctions, and one English auction and compares the auctions on the basis of several measures, including efficiency, price information revelation, and ability to handle repeated bidding and agent learning.
Village Ecodynamics Project
ipem | Published Friday, May 13, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The Village Project is designed to help archaeologists understand the factors influencing settlement patterns of small-scale agrarian peoples. Although such societies are becoming increasingly rare, they represent the norm throughout most of the Neolithic period the world over.
Population Control
David Shanafelt | Published Monday, December 13, 2010 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This model looks at the effects of a “control” on agent populations. Much like farmers spraying pesticides/herbicides to manage pest populations, the user sets a control management regiment to be use
Pest dispersion (simplified representation)
François Rebaudo | Published Wednesday, October 27, 2010 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Simplified representation of the model used to present the global model to farmers
Displaying 9 of 59 results Farmers clear search