About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 5 of 55 results for "Saeed Harati" clear search
Agent-based modeling of the spatio-temporal distribution of Sahelian transhumant herds
Cheick Amed Diloma Gabriel TRAORE Etienne DELAY Alassane Bah Djibril Diop | Published Tuesday, May 20, 2025Sahelian transhumance is a seasonal pastoral mobility between the transhumant’s terroir of origin and one or more host terroirs. Sahelian transhumance can last several months and extend over hundreds of kilometers. Its purpose is to ensure efficient and inexpensive feeding of the herd’s ruminants. This paper describes an agent-based model to determine the spatio-temporal distribution of Sahelian transhumant herds and their impact on vegetation. Three scenarios based on different values of rainfall and the proportion of vegetation that can be grazed by transhumant herds are simulated. The results of the simulations show that the impact of Sahelian transhumant herds on vegetation is not significant and that rainfall does not impact the alley phase of transhumance. The beginning of the rainy season has a strong temporal impact on the spatial distribution of transhumant herds during the return phase of transhumance.
MERCURY extension: population
Tom Brughmans | Published Thursday, May 23, 2019This model is an extended version of the original MERCURY model (https://www.comses.net/codebases/4347/releases/1.1.0/ ) . It allows for experiments to be performed in which empirically informed population sizes of sites are included, that allow for the scaling of the number of tableware traders with the population of settlements, and for hypothesised production centres of four tablewares to be used in experiments.
Experiments performed with this population extension and substantive interpretations derived from them are published in:
Hanson, J.W. & T. Brughmans. In press. Settlement scale and economic networks in the Roman Empire, in T. Brughmans & A.I. Wilson (ed.) Simulating Roman Economies. Theories, Methods and Computational Models. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
…
Team Structure and Task Performance
Davide Secchi Martin Neumann | Published Monday, August 05, 2024This model was designed to study resilience in organizations. Inspired by ethnographic work, it follows the simple goal to understand whether team structure affects the way in which tasks are performed. In so doing, it compares the ‘hybrid’ data-inspired structure with three more traditional structures (i.e. hierarchy, flexible/relaxed hierarchy, and anarchy/disorganization).
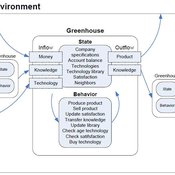
Universal Darwinism in Dutch Greenhouses
Julia Kasmire | Published Wednesday, May 09, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013An ABM, derived from a case study and a series of surveys with greenhouse growers in the Westland, Netherlands. Experiments using this model showshow that the greenhouse horticulture industry displays diversity, adaptive complexity and an uneven distribution, which all suggest that the industry is an evolving system.
The various technologies used inside a Dutch greenhouse interact in combination with an external climate, resulting in an emergent internal climate, which contributes to the final productivity of the greenhouse. This model examines how differing technology development styles affects the overall ability of a community of growers to approach the theoretical maximum yield.
Displaying 5 of 55 results for "Saeed Harati" clear search