About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 483 results from clear search
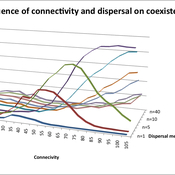
Varying effects of connectivity and dispersal on interacting species dynamics
Kehinde Salau | Published Monday, August 29, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013An agent-based model of species interaction on fragmented landscape is developed to address the question, how do population levels of predators and prey react with respect to changes in the patch connectivity as well as changes in the sharpness of threshold dispersal?
CRESY-I stands for CREativity from a SYstems perspetive, Model I. This is the base model in a series designed to describe a systems approach to creativity in terms of variation, selection and retention (VSR) subprocesses.
A Multi-Agent Simulation Approach to Farmland Auction Markets
James Nolan | Published Wednesday, June 22, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This model explores the effects of agent interaction, information feedback, and adaptive learning in repeated auctions for farmland. It gathers information for three types of sealed-bid auctions, and one English auction and compares the auctions on the basis of several measures, including efficiency, price information revelation, and ability to handle repeated bidding and agent learning.
Village Ecodynamics Project
ipem | Published Friday, May 13, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The Village Project is designed to help archaeologists understand the factors influencing settlement patterns of small-scale agrarian peoples. Although such societies are becoming increasingly rare, they represent the norm throughout most of the Neolithic period the world over.
Replication of ECEC model: Environmental Feedback and the Evolution of Cooperation
Pierre Bommel | Published Tuesday, April 05, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The model, presented here, is a re-implementation of the Pepper and Smuts’ model : - Pepper, J.W. and B.B. Smuts. 2000. “The evolution of cooperation in an ecological context: an agent-based model”. Pp. 45-76 in T.A. Kohler and G.J. Gumerman, eds. Dynamics of human and primate societies: agent-based modeling of social and spatial processes. Oxford University Press, Oxford. - Pepper, J.W. and B.B. Smuts. 2002. “Assortment through Environmental Feedback”. American Naturalist, 160: 205-213 […]
Firm explore-exploit of knowledge
Rosanna Garcia | Published Monday, March 28, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The basic premise of the model is to simulate several ‘agents’ going through build-buy cycles: Build: Factories follow simple rules of strategy in the allocation of resources between making exploration and exploitation type products. Buy: Each of two types of Consumers, early-adopters and late adopters, follow simple purchase decision rules in deciding to purchase a product from one of two randomly chosen factories. Thus, the two working ‘agents’ of the model are ‘factories’ and […]
John Q. Public (JQP): A Model of Political Judgment and Behavior
Sung-Youn Kim | Published Monday, March 14, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The model integrates major theories of political judgment and behavior within the classical cognitive paradigm embedded in the ACT-R cognitive architecture. It models preferences and beliefs of political candidates, parties, and groups.
An empirical ABM for regional land use/cover change: a Dutch case study
Diego Valbuena | Published Saturday, March 12, 2011 | Last modified Thursday, November 11, 2021This is an empirical model described in http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2010.05.001. The objective of the model is to simulate how the decision-making of farmers/agents with different strategies can affect the landscape structure in a region in the Netherlands.
Toward Market Structure as a Complex System: A Web Based Simulation Assignment Implemented in Netlogo
Timothy Kochanski | Published Monday, February 14, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This is the model for a paper that is based on a simulation model, programmed in Netlogo, that demonstrates changes in market structure that occur as marginal costs, demand, and barriers to entry change. Students predict and observe market structure changes in terms of number of firms, market concentration, market price and quantity, and average marginal costs, profits, and markups across the market as firms innovate. By adjusting the demand growth and barriers to entry, students can […]
Displaying 10 of 483 results from clear search