About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers at all levels engage in the establishment and adoption of community standards and good practices for developing and sharing computational models. Model authors can freely publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library alongside narrative documentation, open science metadata, and other emerging open science norms that facilitate software citation, reproducibility, interoperability, and reuse. Model authors can also request peer review of their computational models to receive a DOI.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with additional detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 7 of 7 results social identity clear
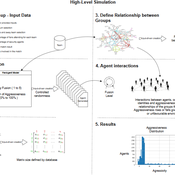
Identity Fusion Group Behaviour Simulator
Leonardo Martins Roberto Cesar Betini | Published Monday, June 03, 2024The model is based on Swann and Buhrmester’s Identity Fusion behavioural theory, which seeks to explain why an individual puts the group’s priorities above their personal expectations. In order to observe the theory and validate group behaviour, a case study was carried out focusing on scenarios of group violence in football stadiums in Brazil. For the modelling, each agent has a distribution of levels of identification with the group to which they belong, with their level of fusion varying between 1 and 5. According to behavioural theory, an individual’s degree of fusion with the group directly interferes with their behaviour of replicating actions and absorbing group beliefs.
Social Identity Model of Protest Emergence (SIMPE)
Cristina Chueca Del Cerro | Published Friday, March 17, 2023The Social Identity Model of Protest Emergence (SIMPE), an agent-based model of national identity and protest mobilisations.
I developed this model for my PhD project, “Polarisation and Protest Mobilisation Around Secessionist Movements: an Agent-Based Model of Online and Offline Social Networks”, at the University of Glasgow (2019-2023).
The purpose of this model is to simulate protest emergence in a given country where there is an independence movement, fostering the self-categorisation process of national identification. In order to contextualised SIMPE, I have used Catalonia, where an ongoing secessionist movement since 2011 has been present, national identity has shown signs of polarisation, and where numerous mobilisations have taken place over the last decade. Data from the Catalan Centre of Opinion Studies (CEO) has been used to inform some of the model parameters.
…
Identity and meat eating behaviour
Jiaqi Ge | Published Thursday, September 29, 2022Using data from the British Social Attitude Survey, we develop an agent-based model to study the effect of social influence on the spread of meat-eating behaviour in the British population.
Social identity approach in a data-driven Axelrod model
alejandrodinkelberg | Published Thursday, July 28, 2022Simulations based on the Axelrod model and extensions to inspect the volatility of the features over time (AXELROD MODEL & Agreement threshold & two model variations based on the Social identity approach)
The Axelrod model is used to predict the number of changes per feature in comparison to the datasets and is used to compare different model variations and their performance.
Input: Real data
…
PA/C model with affinity
Norma Abrica-Jacinto Evguenii Kurmyshev Héctor Juárez | Published Thursday, October 27, 2016We expose RA agent-based model of the opinion and tolerance dynamics in artificial societies. The formal mathematical model is based on the ideas of Social Influence, Social Judgment, and Social Identity theories.
Modeling the Emergence of Riots
Bianica Pires Andrew Crooks | Published Wednesday, January 20, 2016 | Last modified Wednesday, September 21, 2016The purpose of the model is to explore how the unique socioeconomic variables underlying Kibera, local interactions, and the spread of a rumor, may trigger a riot.
Adoption as a social marker
Paul Smaldino | Published Monday, October 17, 2016A model of innovation diffusion in a structured population with two groups who are averse to adopting a produce popular with the outgroup.