About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers at all levels engage in the establishment and adoption of community standards and good practices for developing and sharing computational models. Model authors can freely publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library alongside narrative documentation, open science metadata, and other emerging open science norms that facilitate software citation, reproducibility, interoperability, and reuse. Model authors can also request peer review of their computational models to receive a DOI.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with additional detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 251 results for "Carlos Andrés Chiale" clear search
Peer reviewed SWIRS Spread of a woody invader in riparian systems
Moira Zellner Beatriz Sosa Carlos Andrés Chiale | Published Tuesday, May 09, 2023Riparian forests are one of the most vulnerable ecosystems to the development of biological invasions, therefore limiting their spread is one of the main challenges for conservation. The main factors that explain plant invasions in these ecosystems are the capacity for both short- and long-distance seed dispersion, and the occurrence of suitable habitats that facilitate the establishment of the invasive species. Large floods constitute an abiotic filter for invasion.
This model simulates the spatio-temporal spread of the woody invader Gleditsia. triacanthos in the riparian forest of the National Park Esteros de Farrapos e Islas del Río Uruguay, a riparian system in the coast of the Uruguay river (South America). In this model, we represent different environmental conditions for the development of G. triacanthos, long- and short-distance spread of its fruits, and large floods as the main factor of mortality for fruit and early stages.
Field results show that the distribution pattern of this invasive species is limited by establishment, i.e. it spreads locally through the expansion of small areas, and remotely through new invasion foci. This model recreates this dispersion pattern. We use this model to derive management implications to control the spread of G. triacanthos
Peer reviewed Modelling the Social Complexity of Reputation and Status Dynamics
André Grow Andreas Flache | Published Wednesday, February 01, 2017 | Last modified Wednesday, January 23, 2019The purpose of this model is to illustrate the use of agent-based computational modelling in the study of the emergence of reputation and status beliefs in a population.
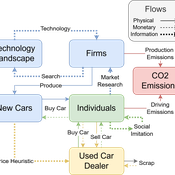
Driving in the wrong direction? A co-evolutionary model of electric vehicle adoption and innovation
Daniel Torren-Peraire | Published Friday, July 11, 2025Car-centric societies face substantial challenges in moving towards sustainable
mobility systems, with internal combustion engine vehicles remaining a major
source of emissions. Electric vehicles play a critical role in addressing this challenge, yet their diffusion depends on the interaction of consumer behaviour, firm
innovation, and policy incentives. This paper develops an agent-based model to
examine these dynamics, calibrated on the data for the state of California over
2001-2023. In the model, heterogeneous car users influenced by their social peers
…
The cultural multiplier of climate policy
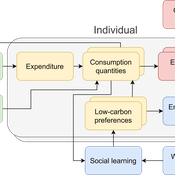
Daniel Torren-Peraire | Published Thursday, October 31, 2024For deep decarbonisation, the design of climate policy needs to account for consumption choices being influenced not only by pricing but also by social learning. This involves changes that pertain to the whole spectrum of consumption, possibly involving shifts in lifestyles. In this regard, it is crucial to consider not just short-term social learning processes but also slower, longer-term, cultural change. Against this background, we analyse the interaction between climate policy and cultural change, focusing on carbon taxation. We extend the notion of “social multiplier” of environmental policy derived in an earlier study to the context of multiple consumer needs while allowing for behavioural spillovers between these, giving rise to a “cultural multiplier”. We develop a model to assess how this cultural multiplier contributes to the effectiveness of carbon taxation. Our results show that the cultural multiplier stimulates greater low-carbon consumption compared to fixed preferences. The model results are of particular relevance for policy acceptance due to the cultural multiplier being most effective at low-carbon tax values, relative to a counter-case of short-term social interactions. Notably, at high carbon tax levels, the distinction between social and cultural multiplier effects diminishes, as the strong price signal drives even resistant individuals toward low-carbon consumption. By varying socio-economic conditions, such as substitutability between low- and high-carbon goods, social network structure, proximity of like-minded individuals and the richness of consumption lifestyles, the model provides insight into how cultural change can be leveraged to induce maximum effectiveness of climate policy.
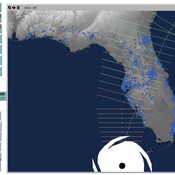
Peer reviewed CHIME ABM Hurricane Evacuation Model
Joshua Watts | Published Friday, March 03, 2017 | Last modified Wednesday, May 29, 2019The CHIME ABM explores information distribution networks and agents’ protective decision making in the context of hurricane landfall.
Peer reviewed CHIME ABM of Hurricane Evacuation
C Michael Barton Sean Bergin Joshua Watts Joshua Alland Rebecca Morss | Published Monday, October 18, 2021 | Last modified Tuesday, January 04, 2022The Communicating Hazard Information in the Modern Environment (CHIME) agent-based model (ABM) is a Netlogo program that facilitates the analysis of information flow and protective decisions across space and time during hazardous weather events. CHIME ABM provides a platform for testing hypotheses about collective human responses to weather forecasts and information flow, using empirical data from historical hurricanes. The model uses real world geographical and hurricane data to set the boundaries of the simulation, and it uses historical hurricane forecast information from the National Hurricane Center to initiate forecast information flow to citizen agents in the model.
Agent-based Line-of-Sight Simulation for safer Crossings (Short Paper - Netlogo Model)
Vincent Franke | Published Thursday, August 05, 2021This software simulates cars and bicycles as traffic participants while crossing different crossroad designs such as roundabouts, protected crossroads and standard crossroads. It is written in Netlogo 6.2 and aims to identify safety characteristics of these layouts using agent-based modeling. Participants track the line of sight to each other and print them as an output alongside with the adjacent destination, used layout, count of collisions/cars/bicycles and time.
Detailed information can be found within the info tab of the program itself.
Agent based modeling of the effects of carbon payments and forest owner cooperatives on carbon storage and revenue in Pacific Northwest forestlands.
Dan Brown Pranab Roy Chowdhury | Published Tuesday, May 09, 2023The Olympic Peninsula ABM works as a virtual laboratory to simulate the existing forestland management practices as followed by different forestland owner groups in the Olympic Peninsula, Washington, and explore how they could shape the future provisions of multifunctional ecosystem services such as Carbon storage and revenue generation under the business-as-usual scenario as well as by their adaptation to interventions. Forestlands are socio-ecological systems that interact with economic, socio-cultural, and policy systems. Two intervention scenarios were introduced in this model to simulate the adaptation of landowner behavior and test the efficacy of policy instruments in promoting sustainable forest practices and fostering Carbon storage and revenue generation. (1) A market-linked carbon offset scheme that pays the forestland owners a financial incentive in the form of a yearly carbon rent. (2) An institutional intervention policy that allows small forest owners (SFLO) to cooperate for increased market access and benefits under carbon rent scenario. The model incorporates the heterogeneous contexts within which the forestland owners operate and make their forest management decisions by parameterizing relevant agent attributes and contextualizing their unique decision-making processes.
ManPest
François Rebaudo | Published Tuesday, February 25, 2014 | Last modified Wednesday, August 27, 2014The purpose of the model is to explore the impacts of global change on the ability of a community of farmers to adapt their practices to an agricultural pest.
MCA-SdA (ABM of mining-community-aquifer interactions in Salar de Atacama, Chile)
Wenjuan Liu | Published Tuesday, December 01, 2020 | Last modified Thursday, November 04, 2021This model represnts an unique human-aquifer interactions model for the Li-extraction in Salar de Atacama, Chile. It describes the local actors’ experience of mining-induced changes in the socio-ecological system, especially on groundwater changes and social stressors. Social interactions are designed specifically according to a long-term local fieldwork by Babidge et al. (2019, 2020). The groundwater system builds on the FlowLogo model by Castilla-Rho et al. (2015), which was then parameterized and calibrated with local hydrogeological inputs in Salar de Atacama, Chile. The social system of the ABM is defined and customozied based on empirical studies to reflect three major stressors: drought stress, population stress, and mining stress. The model reports evolution of groundwater changes and associated social stress dynamics within the modeled time frame.
Displaying 10 of 251 results for "Carlos Andrés Chiale" clear search