About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 105 results for "I Nikolic" clear search
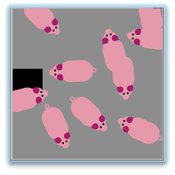
Tail biting behaviour in pigs
Iris J.M.M. Boumans Iris Jmm Boumans | Published Friday, April 22, 2016 | Last modified Wednesday, September 14, 2016The model simulates tail biting behaviour in pigs and how they can turn into a biter and/or victim. The effect of a redirected motivation, behavioural changes in victims and preference to bite a lying pig on tail biting can be tested in the model
Wave When the Hale Wale (WWHW)
María Pereda José Manuel Galán Iván Briz I Godino Jorge Caro Débora Zurro Myriam Álvarez José Santos | Published Friday, October 10, 2014 | Last modified Wednesday, April 25, 2018WWHW is an agent-based model designed to allow the exploration of the emergence, resilience and evolution of cooperative behaviours in hunter-fisher-gatherer societies.
Multi-level model of attitudinal dynamics
Ingo Wolf | Published Wednesday, April 06, 2016 | Last modified Wednesday, May 04, 2016A model of attitudinal dynamics based on the cognitive mechanism of emotional coherence. The code is written in Java. For initialization an additional dataset is required.
LAMDA - Learning Agents for Mechanism-Design Analysis
Iris Lorscheid Matthias Meyer | Published Monday, August 08, 2016The simulation model LAMDA investigates the influences of varying cognitive abilities of the decision maker on the truth-inducing effect of the Groves mechanism. Bounded rationality concepts are represented by information states and learning models.
The MOBILITY model analyzes how agents’ mobility affects the performance of social-ecological systems in different landscape configurations.
Demand Planning Model
Iris Lorscheid Jonas Hauke Matthias Meyer | Published Wednesday, October 04, 2017Demand planning requires processing of distributed information. In this process, individuals, their properties and interactions play a crucial role. This model is a computational testbed to investigate these aspects with respect to forecast accuracy.
A model on feeding and social interaction behaviour of pigs
Iris J.M.M. Boumans | Published Thursday, May 04, 2017 | Last modified Tuesday, February 27, 2018The model simulates interaction between internal physiological factors (e.g. energy balance) and external social factors (e.g. competition level) underlying feeding and social interaction behaviour of commercially group-housed pigs.
PSMED - Patagonia Simple Model of Ethnic Differentiation
Xavier Vilà Joan A Barceló J A Cuesta Florencia Del Castillo Ricardo Del Olmo José M Galán Laura Mameli Francisco J Miguel David Poza José I Santos | Published Tuesday, December 10, 2013Patagonia PSMED is an agent-based model designed to study a simple case of Evolution of Ethnic Differentiation. It replicates how can hunter-gatherer societies evolve and built cultural identities as a consequence of the way they interacted.
A spatial model of resource-consumer dynamics
Arend Ligtenberg Guus Ten Broeke George Ak Van Voorn Jaap Molenaar | Published Wednesday, January 11, 2017 | Last modified Thursday, September 17, 2020The model simulates agents in a spatial environment competing for a common resource that grows on patches. The resource is converted to energy, which is needed for performing actions and for surviving.
Coalitions in Networked Innovation
Rory Sie Peter Sloep Marlies Bitter-Rijpkema | Published Tuesday, February 11, 2014A first version of a model that describes how coalitions are formed during open, networked innovation
Displaying 10 of 105 results for "I Nikolic" clear search