About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 934 results for "George Ak Van Voorn" clear search
This is an agent-based model that simulates the structural evolution in food supply chain.
Model supporting the serious game RÁC
Patrick Taillandier Alexis Drogoul Léo Biré | Published Thursday, January 25, 2024This model is supporting the serious game RÁC (“waste” in Vietnamese), dedicated to foster discussion about solid waste management in a Vietnamese commune in the Bắc Hưng Hải irrigation system.
The model is replicating waste circulation and environmental impact in four fictive villages. During the game, the players take actions and see how their decisions have an impact on the model.
This model was implemented using the GAMA platform, using gaml language.
Social Construction of Reality Agent-Based Model
Manuel Castañón-Puga E. Dante Suarez Loren Demerath | Published Saturday, June 29, 2024This model illustrates the processes underlying the social construction of reality through an agent-based genetic algorithm. By simulating the interactions of agents within a structured environment, we have demonstrated how shared information and popularity contribute to the formation of emergent social structures with diverse cultures. The model illustrates how agents balance environmentally valid information with socially reliable information. It also highlights how social interaction leads to the formation of stable, yet diverse, social groups.
Peer reviewed Viable North Sea (ViNoS): A NetLogo Agent-based Model of German Small-scale Fisheries
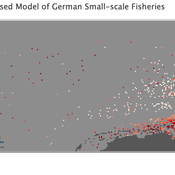
Wolfgang Nikolaus Probst Jieun Seo Jürgen Scheffran Carsten Lemmen Sascha Hokamp Verena Mühlberger Serra Örey | Published Thursday, May 25, 2023 | Last modified Tuesday, December 05, 2023Viable North Sea (ViNoS) is an Agent-based Model of the German North Sea Small-scale Fisheries in a Social-Ecological Systems framework focussing on the adaptive behaviour of fishers facing regulatory, economic, and resource changes. Small-scale fisheries are an important part both of the cultural perception of the German North Sea coast and of its fishing industry. These fisheries are typically family-run operations that use smaller boats and traditional fishing methods to catch a variety of bottom-dwelling species, including plaice, sole, and brown shrimp. Fisheries in the North Sea face area competition with other uses of the sea – long practiced ones like shipping, gas exploration and sand extractions, and currently increasing ones like marine protection and offshore wind farming. German authorities have just released a new maritime spatial plan implementing the need for 30% of protection areas demanded by the United Nations High Seas Treaty and aiming at up to 70 GW of offshore wind power generation by 2045. Fisheries in the North Sea also have to adjust to the northward migration of their established resources following the climate heating of the water. And they have to re-evaluate their economic balance by figuring in the foreseeable rise in oil price and the need for re-investing into their aged fleet.
Lifestyle tradeoffs and the decline of well-being
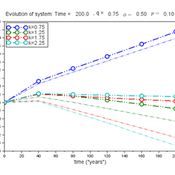
Chris Thron | Published Friday, January 01, 2016Scilab version of an agent-based model of societal well-being, based on the factors of: overvaluation of conspicuous prosperity; tradeoff rate between inconspicuous/conspicuous well-being factors; turnover probability; and individual variation.
Bicycle encounter model
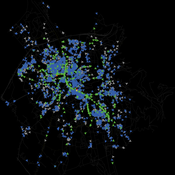
Gudrun Wallentin | Published Saturday, October 29, 2016 | Last modified Friday, March 29, 2019This Bicycle encounter model builds on the Salzburg Bicycle model (Wallentin & Loidl, 2015). It simulates cyclist flows and encounters, which are locations of potential accidents between cyclists.
Animal territory formation (Reusable Building Block RBB)
Volker Grimm Stephanie Kramer-Schadt Robert Zakrzewski | Published Sunday, November 12, 2023This is a generic sub-model of animal territory formation. It is meant to be a reusable building block, but not in the plug-and-play sense, as amendments are likely to be needed depending on the species and region. The sub-model comprises a grid of cells, reprenting the landscape. Each cell has a “quality” value, which quantifies the amount of resources provided for a territory owner, for example a tiger. “Quality” could be prey density, shelter, or just space. Animals are located randomly in the landscape and add grid cells to their intial cell until the sum of the quality of all their cells meets their needs. If a potential new cell to be added is owned by another animal, competition takes place. The quality values are static, and the model does not include demography, i.e. mortality, mating, reproduction. Also, movement within a territory is not represented.
UK Demographic Simulator
Tony Lawson | Published Monday, February 27, 2012 | Last modified Tuesday, October 21, 2014A dynmaic microsimulation model to project the UK population over time
Multi-agent modeling and analysis of the knowledge learning of a human-machine hybrid intelligent organization with human-machine trust
Haoxiang Zhang | Published Monday, April 24, 2023Machine learning technologies have changed the paradigm of knowledge discovery in organizations and transformed traditional organizational learning to human-machine hybrid intelligent organizational learning. However, it remains unclear how human-machine trust, which is an important factor that influences human-machine knowledge exchange, affects the effectiveness of human-machine hybrid intelligent organizational learning. To explore this issue, we used multi-agent simulation to construct a knowledge learning model of a human-machine hybrid intelligent organization with human-machine trust.
Peer reviewed AgentEx
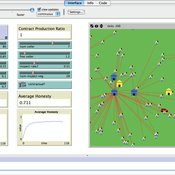
Nanda Wijermans Maja Schlüter Caroline Schill Therese Lindahl | Published Sunday, November 13, 2016AgentEx aims to advance understanding of group processes for sustainable management of a common pool resource (CPR). By supporting the development and test explanations of cooperation and sustainable exploitation.
Displaying 10 of 934 results for "George Ak Van Voorn" clear search