About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 444 results simulation clear search
Peer reviewed The Viability of the Social-Ecological Agroecosystem (ViSA) Spatial Agent-based Model
Mostafa Shaaban | Published Monday, March 25, 2024ViSA 2.0.0 is an updated version of ViSA 1.0.0 aiming at integrating empirical data of a new use case that is much smaller than in the first version to include field scale analysis. Further, the code of the model is simplified to make the model easier and faster. Some features from the previous version have been removed.
It simulates decision behaviors of different stakeholders showing demands for ecosystem services (ESS) in agricultural landscape. It investigates conditions and scenarios that can increase the supply of ecosystem services while keeping the viability of the social system by suggesting different mixes of initial unit utilities and decision rules.
Agent-based tax evasion model for investigating impacts of public disclosure
Hiroyuki Sano | Published Thursday, March 14, 2024The model explores the impact of public disclosure on tax compliance among diverse agents, including individual taxpayers and a tax authority. It incorporates heterogeneous preferences and income endowments among taxpayers, captured through a utility function that considers psychic costs subtracted from expected pecuniary utility. These costs include moral, reciprocity, and stigma costs associated with norm violations, leading to variations in taxpayers’ risk attitudes and related parameters. The tax authority’s attributes, such as the frequency of random audits, penalty rate, and the choice between partial or full disclosure, remain fixed throughout the simulation. Income endowments and preference parameters are randomly assigned to taxpayers at the outset.
Taxpayers maximize their expected utility by reporting income, taking into account tax, penalty, and audit rates. They make annual decisions based on their own and their peers’ behaviors from the previous year. Taxpayers indirectly interact at the societal level through public disclosure conducted by the tax authority, exchanging tax information among peers. Each period in the simulation collects data on total reported income, average compliance rates per income group, distribution of compliance rates, counts of compliers, full evaders, partial evaders, and the numbers of taxpayers experiencing guilt and anger. The model evaluates whether public disclosure positively or negatively impacts compliance rates and quantifies this impact based on aggregated individual reporting behaviors.
Evaluate government policies for farmers’ adoption and synergy in improving irrigation systems
Amir Hajimirzajan | Published Sunday, February 25, 2024The ABM model is designed to model the adaptability of farmers in DTIM. This model includes two groups of farmers and local government admins agents. Farmers with different levels, with low WP of DTIM, are looking for economic benefits and reduced irrigation and production costs. Meanwhile, the government is looking for strategic goals to maintain water resources’ sustainability. The local government admins employ incentives (subsidies in this study) to encourage farmers to DTIM. In addition, it is used as a tool for supervision and training farmers’ performance. Farmers are currently harvesting water resources with irrigation systems and different levels of technology, and they intend to provide short-term benefits. Farmers adjust the existing approach based on their knowledge of the importance of DTIM and propensity to increase WP and cost-benefit evaluation. DTIM has an initial implementation fee. Every farmer can increase WP by using government subsidies. If none of the farmers create optimal use of water resources, access to water resources will be threatened in the long term. This is considered a hypothetical cost for farmers who do not participate in DTIM. With DTIM, considering that local government admins’ facilities cover an essential part of implementation costs, farmers may think of profiting from local government admins’ facilities by selling that equipment, especially if the farmers in the following conditions may consider selling their developed irrigation equipment. In this case, the technology of their irrigation system will return to the state before development.
- When the threshold of farmers’ propensity to DTIM is low (for example, in the conditions of scarcity of access to sufficient training about the new irrigation system or its role in reducing the cost and sustainability of water resources)
- When the share of government subsidy is high, and as a result, the profit from the sale of equipment is attractive, especially in conditions of inflation.
- Finally, farmers’ honesty threshold should be reduced based on the positive experience of profit-seeking and deception among neighbors.
Increasing the share of government subsidies can encourage farmers to earn profits. Therefore, the government can help increase farmers’ profits by considering the assessment teams at different levels with DTIM training . local government admins evaluations monitor the behavior of farmers. If farmers sell their improved irrigation system for profit, they may be deprived of some local government admins’ services and the possibility of receiving subsidies again. Assessments The local government admins can increase farmers’ honesty. Next, the ABM model evaluates local government admins policies to achieve a suitable framework for water resources management in the Miandoab region.
Peer reviewed MADTOR: Model for Assessing Drug Trafficking Organizations Resilience
Deborah Manzi | Published Friday, February 23, 2024 | Last modified Friday, February 27, 2026Criminal organizations operate in complex changing environments. Being flexible and dynamic allows criminal networks not only to exploit new illicit opportunities but also to react to law enforcement attempts at disruption, enhancing the persistence of these networks over time. Most studies investigating network disruption have examined organizational structures before and after the arrests of some actors but have disregarded groups’ adaptation strategies.
MADTOR simulates drug trafficking and dealing activities by organized criminal groups and their reactions to law enforcement attempts at disruption. The simulation relied on information retrieved from a detailed court order against a large-scale Italian drug trafficking organization (DTO) and from the literature.
The results showed that the higher the proportion of members arrested, the greater the challenges for DTOs, with higher rates of disrupted organizations and long-term consequences for surviving DTOs. Second, targeting members performing specific tasks had different impacts on DTO resilience: targeting traffickers resulted in the highest rates of DTO disruption, while targeting actors in charge of more redundant tasks (e.g., retailers) had smaller but significant impacts. Third, the model examined the resistance and resilience of DTOs adopting different strategies in the security/efficiency trade-off. Efficient DTOs were more resilient, outperforming secure DTOs in terms of reactions to a single, equal attempt at disruption. Conversely, secure DTOs were more resistant, displaying higher survival rates than efficient DTOs when considering the differentiated frequency and effectiveness of law enforcement interventions on DTOs having different focuses in the security/efficiency trade-off.
Overall, the model demonstrated that law enforcement interventions are often critical events for DTOs, with high rates of both first intention (i.e., DTOs directly disrupted by the intervention) and second intention (i.e., DTOs terminating their activities due to the unsustainability of the intervention’s short-term consequences) culminating in dismantlement. However, surviving DTOs always displayed a high level of resilience, with effective strategies in place to react to threatening events and to continue drug trafficking and dealing.
Peer reviewed Deforestation
MohammadAli Aghajani | Published Saturday, January 20, 2024 | Last modified Thursday, August 14, 2025Deforestation Simulation Model in NetLogo with GIS Layers
This model has developed in Netlogo software and utilizes
the GIS extension.
This NetLogo-based agent-based model (ABM) simulates deforestation dynamics using the GIS extension. It incorporates parameters like wood extraction, forest regeneration, agricultural expansion, and livestock impact. The model integrates spatial layers, including forest areas, agriculture zones, rural settlements, elevation, slope, and livestock distribution. Outputs include real-time graphical representations of forest loss, regeneration, and land-use changes. This model helps analyze deforestation patterns and conservation strategies using ABM and GIS.
Role of Diversity in Team Performance: the Case of Missing Expertise, an Agent Based Simulations
Tamás Kiss | Published Friday, December 29, 2023This ABM simulates problem solving agents as they work on a set of tasks. Each agent has a trait vector describing their skills. Two agents might form a collaboration if their traits are similar enough. Tasks are defined by a component vector. Agents work on tasks by decreasing tasks’ component vectors towards zero.
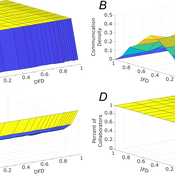
The simulation generates agents with given intrapersonal functional diversity (IFD), and dominant function diversity (DFD), and a set of random tasks and evaluates how agents’ traits influence their level of communication and the performance of a team of agents.
Modeling results highlight the importance of the distributions of agents’ properties forming a team, and suggests that for a thorough description of management teams, not only diversity measures based on individual agents, but an aggregate measure is also required.
…
Seascapes of the Unreal: Using Agent Based Modeling to Examine Traditional Coast Salish Maritime Mobility
Adam Rorabaugh | Published Friday, December 22, 2023Non-traditional tools and mediums can provide unique methodological and interpretive opportunities for archaeologists. In this case, the Unreal Engine (UE), which is typically used for games and media, has provided a powerful tool for non-programmers to engage with 3D visualization and programming as never before. UE has a low cost of entry for researchers as it is free to download and has user-friendly “blueprint” tools that are visual and easily extendable. Traditional maritime mobility in the Salish Sea is examined using an agent-based model developed in blueprints. Focusing on the sea canoe travel of the Straits Salish northwestern Washington State and southwest British Columbia. This simulation integrates GIS data to assess travel time between Coast Salish archaeological village locations and archaeologically represented resource gathering areas. Transportation speeds informed by ethnographic data were used to examine travel times for short forays and longer inter-village journeys. The results found that short forays tended to half day to full day trips when accounting for resource gathering activities. Similarly, many locations in the Salish Sea were accessible in long journeys within two to three days, assuming fair travel conditions. While overall transportation costs to reach sites may be low, models such as these highlight the variability in transport risk and cost. The integration of these types of tools, traditionally used for entertainment, can increase the accessibility of modeling approaches to researchers, be expanded to digital storytelling, including aiding in the teaching of traditional ecological knowledge and placenames, and can have wide applications beyond maritime archaeology.
This is v0.01 of a UE5.2.1 agent based model.
IUCM - The Integrated Urban Complexity Model
Roger Cremades Philipp S. Sommer | Published Thursday, December 14, 2023We present the Integrated Urban Complexity model (IUCm 1.0) that computes “climate-smart urban forms”, which are able to cut emissions related to energy consumption from urban mobility in half. Furthermore, we show the complex features that go beyond the normal debates about urban sprawl vs. compactness. Our results show how to reinforce fractal hierarchies and population density clusters within climate risk constraints to significantly decrease the energy consumption of urban mobility. The new model that we present aims to produce new advice about how cities can combat climate change. From a technical angle, this model is a geographical automaton, conceptually interfacing between cellular automata and spatial explicit optimisation to achieve normative sustainability goals related to low energy. See a complete user guide at https://iucm.readthedocs.io/en/latest/ .
Peer reviewed Credit and debt market of low-income families
Márton Gosztonyi | Published Tuesday, December 12, 2023 | Last modified Friday, January 19, 2024The purpose of the Credit and debt market of low-income families model is to help the user examine how the financial market of low-income families works.
The model is calibrated based on real-time data which was collected in a small disadvantaged village in Hungary it contains 159 households’ social network and attributes data.
The simulation models the households’ money liquidity, expenses and revenue structures as well as the formal and informal loan institutions based on their network connections. The model forms an intertwined system integrated in the families’ local socioeconomic context through which families handle financial crises and overcome their livelihood challenges from one month to another.
The simulation-based on the abstract model of low-income families’ financial survival system at the bottom of the pyramid, which was described in following the papers:
…
Schwartz Human Values and the Economic Performance
Marcin Czupryna Bogumił Kamiński | Published Wednesday, November 29, 2023The purpose of the model is to provide an analogy for how the Schwartz values may influence the aggregated economic performance, as measured by: public goods provision, private goods provision and leisure time.
Displaying 10 of 444 results simulation clear search