About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 853 results for "Jes%C3%BAs M Zamarre%C3%B1o" clear search
word-of-mouth dynamics with information seeking
Samuel Thiriot | Published Wednesday, October 24, 2018Studies on word-of-mouth identify two behaviors leading to transmission of information between individuals: proactive transmission of information, and information seeking. Individuals who are aware might be curious of it and start seeking for information; they might find around them the expertise held by another individual. Field studies indicate individuals do not adopt an innovation if they don’t hold the corresponding expertise. This model describes this information seeking behavior, and enables the exploration of the dynamics which emerges out of it.
Peer reviewed Emergent Firms Model
J M Applegate | Published Friday, July 13, 2018The Emergent Firm (EF) model is based on the premise that firms arise out of individuals choosing to work together to advantage themselves of the benefits of returns-to-scale and coordination. The Emergent Firm (EF) model is a new implementation and extension of Rob Axtell’s Endogenous Dynamics of Multi-Agent Firms model. Like the Axtell model, the EF model describes how economies, composed of firms, form and evolve out of the utility maximizing activity on the part of individual agents. The EF model includes a cash-in-advance constraint on agents changing employment, as well as a universal credit-creating lender to explore how costs and access to capital affect the emergent economy and its macroeconomic characteristics such as firm size distributions, wealth, debt, wages and productivity.
Peer reviewed General Housing Model
J M Applegate | Published Thursday, May 07, 2020The General Housing Model demonstrates a basic housing market with bank lending, renters, owners and landlords. This model was developed as a base to which students contributed additional functions during Arizona State University’s 2020 Winter School: Agent-Based Modeling of Social-Ecological Systems.
Peer reviewed Virus Transmission with Super-spreaders
J M Applegate | Published Saturday, September 11, 2021A curious aspect of the Covid-19 pandemic is the clustering of outbreaks. Evidence suggests that 80\% of people who contract the virus are infected by only 19% of infected individuals, and that the majority of infected individuals faile to infect another person. Thus, the dispersion of a contagion, $k$, may be of more use in understanding the spread of Covid-19 than the reproduction number, R0.
The Virus Transmission with Super-spreaders model, written in NetLogo, is an adaptation of the canonical Virus Transmission on a Network model and allows the exploration of various mitigation protocols such as testing and quarantines with both homogenous transmission and heterogenous transmission.
The model consists of a population of individuals arranged in a network, where both population and network degree are tunable. At the start of the simulation, a subset of the population is initially infected. As the model runs, infected individuals will infect neighboring susceptible individuals according to either homogenous or heterogenous transmission, where heterogenous transmission models super-spreaders. In this case, k is described as the percentage of super-spreaders in the population and the differing transmission rates for super-spreaders and non super-spreaders. Infected individuals either recover, at which point they become resistant to infection, or die. Testing regimes cause discovered infected individuals to quarantine for a period of time.
Peer reviewed Modern Wage Dynamics
J M Applegate | Published Sunday, June 05, 2022The Modern Wage Dynamics Model is a generative model of coupled economic production and allocation systems. Each simulation describes a series of interactions between a single aggregate firm and a set of households through both labour and goods markets. The firm produces a representative consumption good using labour provided by the households, who in turn purchase these goods as desired using wages earned, thus the coupling.
Each model iteration the firm decides wage, price and labour hours requested. Given price and wage, households decide hours worked based on their utility function for leisure and consumption. A labour market construct chooses the minimum of hours required and aggregate hours supplied. The firm then uses these inputs to produce goods. Given the hours actually worked, the households decide actual consumption and a market chooses the minimum of goods supplied and aggregate demand. The firm uses information gained through observing market transactions about consumption demand to refine their conceptions of the population’s demand.
The purpose of this model is to explore the general behaviour of an economy with coupled production and allocation systems, as well as to explore the effects of various policies on wage and production, such as minimum wage, tax credits, unemployment benefits, and universal income.
…
Recycling behavior of Chinese households
Igor Nikolic B Dijkhuizen M Van Den Hoven M Minderhoud N Wäckerlin | Published Monday, June 19, 2017 | Last modified Thursday, March 29, 2018The model represents empirically observed recycling behaviour of Chinese citizens, based on the theory of reasoned action (TRA), the theory of planned behaviour (TPB) and the theory of planned behaviour extended with situational factors (TPB+).
Peer reviewed Modelling Agricultural Innovations as a Social-Ecological Phenomenon
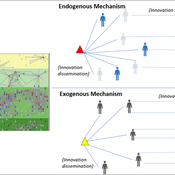
Maja Schlüter Udita Sanga | Published Thursday, November 17, 2022The goal of the AG-Innovation agent-based model is to explore and compare the effects of two alternative mechanisms of innovation development and diffusion (exogenous, linear and endogenous, non-linear) on emergent properties of food and income distribution and adoption rates of different innovations. The model also assesses the range of conditions under which these two alternative mechanisms would be effective in improving food security and income inequality outcomes. Our modelling questions were: i) How do cross-scalar social-ecological interactions within agricultural innovation systems affect system outcomes of food security and income inequality? ii) Do foreign aid-driven exogenous innovation perpetuate income inequality and food insecurity and if so, under which conditions? iii) Do community-driven endogenous innovations improve food security and income inequality and if so, under which conditions? The Ag-Innovation model is intended to serve as a thinking tool for for the development and testing of hypotheses, generating an understanding of the behavior of agricultural innovation systems, and identifying conditions under which alternated innovation mechanisms would improve food security and income inequality outcomes.
The conditional defector strategy can violate the most crucial supporting mechanisms of cooperation.
Ahmed Ibrahim | Published Tuesday, June 07, 2022 | Last modified Sunday, September 28, 2025Cooperation is essential for all domains of life. Yet, ironically, it is intrinsically vulnerable to exploitation by cheats. Hence, an explanatory necessity spurs many evolutionary biologists to search for mechanisms that could support cooperation. In general, cooperation can emerge and be maintained when cooperators are sufficiently interacting with themselves. This communication provides a kind of assortment and reciprocity. The most crucial and common mechanisms to achieve that task are kin selection, spatial structure, and enforcement (punishment). Here, we used agent-based simulation models to investigate these pivotal mechanisms against conditional defector strategies. We concluded that the latter could easily violate the former and take over the population. This surprising outcome may urge us to rethink the evolution of cooperation, as it illustrates that maintaining cooperation may be more difficult than previously thought. Moreover, empirical applications may support these theoretical findings, such as invading the cooperator population of pathogens by genetically engineered conditional defectors, which could be a potential therapy for many incurable diseases.
Peer reviewed Are Countertrade credits as flexible and efficient as cash? A novel approach to reducing income inequality using countertrade methodology.
Peter Malliaros | Published Monday, May 03, 2021 | Last modified Tuesday, May 11, 2021The impacts of income inequality can be seen everywhere, regardless of the country or the level of economic development. According to the literature review, income inequality has negative impacts in economic, social, and political variables. Notwithstanding of how well or not countries have done in reducing income inequality, none have been able to reduce it to a Gini Coefficient level of 0.2 or less.
This is the promise that a novel approach called Counterbalance Economics (CBE) provides without the need of increased taxes.
Based on the simulation, introducing the CBE into the Australian, UK, US, Swiss or German economies would result in an overall GDP increase of under 1% however, the level of inequality would be reduced from an average of 0.33 down to an average of 0.08. A detailed explanation of how to use the model, software, and data dependencies along with all other requirements have been included as part of the info tab in the model.
Confirmation Bias improves Performance in a Signal Detection Task and evolves in an Evolutionary Algorithm
Michael Vogrin | Published Monday, May 08, 2023Confirmation Bias is usually seen as a flaw of the human mind. However, in some tasks, it may also increase performance. Here, agents are confronted with a number of binary Signals (A, or B). They have a base detection rate, e.g. 50%, and after they detected one signal, they get biased towards this type of signal. This means, that they observe that kind of signal a bit better, and the other signal a bit worse. This is moderated by a variable called “bias_effect”, e.g. 10%. So an agent who detects A first, gets biased towards A and then improves its chance to detect A-signals by 10%. Thus, this agent detects A-Signals with the probability of 50%+10% = 60% and detects B-Signals with the probability of 50%-10% = 40%.
Given such a framework, agents that have the ability to be biased have better results in most of the scenarios.
Displaying 10 of 853 results for "Jes%C3%BAs M Zamarre%C3%B1o" clear search