About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 121 results for "Manuel Scholz-Wäckerle" clear search
An Agent-Based DSS for Word-of-Mouth Programs in Freemium Apps
Manuel Chica | Published Monday, September 05, 2016An agent-based framework that aggregates social network-level individual interactions to run targeting and rewarding programs for a freemium social app. Git source code in https://bitbucket.org/mchserrano/socialdynamicsfreemiumapps
Aspiration, Attainment and Success: An agent-based model of distance-based school allocation
James Millington | Published Friday, November 02, 2012 | Last modified Friday, July 03, 2015The purpose of this model is to investigate mechanisms driving the geography of educational inequality and the consequences of these mechanisms for individuals with varying attributes and mobility.
ABM Household Decision Making on Solar Energy using Theory of Planned Behaviour
Tatiana Filatova Hannah Muelder | Published Tuesday, May 21, 2019The model aims at estimating household energy consumption and the related greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions reduction based on the behavior of the individual household under different operationalizations of the Theory of Planned Behaviour (TPB).
The original model is developed as a tool to explore households decisions regarding solar panel investments and cumulative consequences of these individual choices (i.e. diffusion of PVs, regional emissions savings, monetary savings). We extend the model to explore a methodological question regarding an interpretation of qualitative concepts from social science theories, specifically Theory of Planned Behaviour in a formal code of quantitative agent-based models (ABMs). We develop 3 versions of the model: one TPB-based ABM designed by the authors and two alternatives inspired by the TPB-ABM of Schwarz and Ernst (2009) and the TPB-ABM of Rai and Robinson (2015). The model is implemented in NetLogo.
Modeling financial networks based on interpersonal trust
Michael Roos Anna Klabunde | Published Wednesday, May 29, 2013 | Last modified Thursday, November 28, 2013We build a stylized model of a network of business angel investors and start-up entrepreneurs. Decisions are based on trust as a decision making tool under true uncertainty.
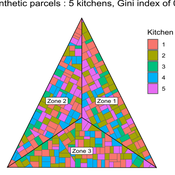
MeReDiem : Fallow Land Simulations to examine the conditions of sustainable village livelihood
Etienne DELAY Paul Chapron Mathieu | Published Monday, January 20, 2025 | Last modified Tuesday, January 21, 2025The MeReDiem model aims to simulate the effect of socio-agricultural practices of farmers and pastors on the food sustainability and soil fertility of a serrer village, in Senegal. The model is a central part of a companion modeling and exploration approach, described in a paper, currently under review)
The village population is composed of families (kitchens). Kitchens cultivate their land parcels to feed their members, aiming for food security at the family level. On a global level , the village tries to preserve the community fallow land as long as possible.
Kitchens sizes vary depending on the kitchens food production, births and migration when food is insufficient.
…
MTC_Model_Pilditch&Madsen
Toby Pilditch | Published Friday, October 09, 2020Micro-targeted vs stochastic political campaigning agent-based model simulation. Written by Toby D. Pilditch (University of Oxford, University College London), in collaboration with Jens K. Madsen (University of Oxford, London School of Economics)
The purpose of the model is to explore the various impacts on voting intention among a population sample, when both stochastic (traditional) and Micto-targeted campaigns (MTCs) are in play. There are several stages of the model: initialization (setup), campaigning (active running protocols) and vote-casting (end of simulation). The campaigning stage consists of update cycles in which “voters” are targeted and “persuaded” - updating their beliefs in the campaign candidate / policies.
Relative Agreement Model and Network Structure
Spiro Maroulis David Adelberg | Published Friday, January 29, 2016This adaptation of the Relative Agreement model of opinion dynamics (Deffuant et al. 2002) extends the Meadows and Cliff (2012) implementation of this model in a manner that explores the effect of the network structure among the agents.
Network Behaviour Diffusion
Jennifer Badham | Published Saturday, October 02, 2021This model implements two types of network diffusion from an initial group of activated nodes. In complex contagion, a node is activated if the proportion of neighbour nodes that are already activated exceeds a given threshold. This is intended to represented the spread of health behaviours. In simple contagion, an activated node has a given probability of activating its inactive neighbours and re-tests each time step until all of the neighbours are activated. This is intended to represent information spread.
A range of networks are included with the model from secondary school friendship networks. The proportion of nodes initially activated and the method of selecting those nodes are controlled by the user.
Peer reviewed Casting: A Bio-Inspired Method for Restructuring Machine Learning Ensembles
Colin Lynch Bryan Daniels | Published Thursday, September 18, 2025The wisdom of the crowd refers to the phenomenon in which a group of individuals, each making independent decisions, can collectively arrive at highly accurate solutions—often more accurate than any individual within the group. This principle relies heavily on independence: if individual opinions are unbiased and uncorrelated, their errors tend to cancel out when averaged, reducing overall bias. However, in real-world social networks, individuals are often influenced by their neighbors, introducing correlations between decisions. Such social influence can amplify biases, disrupting the benefits of independent voting. This trade-off between independence and interdependence has striking parallels to ensemble learning methods in machine learning. Bagging (bootstrap aggregating) improves classification performance by combining independently trained weak learners, reducing bias. Boosting, on the other hand, explicitly introduces sequential dependence among learners, where each learner focuses on correcting the errors of its predecessors. This process can reinforce biases present in the data even if it reduces variance. Here, we introduce a new meta-algorithm, casting, which captures this biological and computational trade-off. Casting forms partially connected groups (“castes”) of weak learners that are internally linked through boosting, while the castes themselves remain independent and are aggregated using bagging. This creates a continuum between full independence (i.e., bagging) and full dependence (i.e., boosting). This method allows for the testing of model capabilities across values of the hyperparameter which controls connectedness. We specifically investigate classification tasks, but the method can be used for regression tasks as well. Ultimately, casting can provide insights for how real systems contend with classification problems.
Bargaining with misvaluation
Marcin Czupryna | Published Wednesday, January 14, 2026Subjective biases and errors systematically affect market equilibria, whether at the population level or in bilateral trading. Here, we consider the possibility that an agent engaged in bilateral trading is mistaken about her own valuation of the good she expects to trade, that has not been explicitly incorporated into the existing bilateral trade literature. Although it may sound paradoxical that a subjective private valuation is something an agent can be mistaken about, as it is up to her to fix it, we consider the case in which that agent, seller or buyer, consciously or not, given the structure of a market, a type of good, and a temporary lack of information, may arrive at an erroneous valuation. The typical context through which this possibility may arise is in relation with so-called experience goods, which are sold while all their intrinsic qualities are still unknown (such as untasted bottled fine wines). We model this “private misvaluation” phenomenon in our study. The agents may also be mistaken about how their exchange counterparties are themselves mistaken. Formally, they attribute a certain margin of error to the other agent, which can differ from the actual way that another agent misvalues the good under consideration. This can constitute the source of a second-order misvaluation. We model different attitudes and situations in which agents face unexpected signals from their counterparties and the manner and extent to which they revise their initial beliefs. We analyse and simulate numerically the consequences of first-order and second-order misvaluation on market equilibria.
Displaying 10 of 121 results for "Manuel Scholz-Wäckerle" clear search