About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 53 results for "Jose María Cela" clear search
We propose here a computational model of school segregation that is aligned with a corresponding Schelling-type model of residential segregation. To adapt the model for application to school segregation, we move beyond previous work by combining two preference arguments in modeling parents’ school choice, preferences for the ethnic composition of a school and preferences for minimizing the travelling distance to the school.
Peer reviewed SIM-VOLATILE: Adoption of emerging circular technologies in the waste-treatment sector
Siavash Farahbakhsh | Published Wednesday, December 14, 2022The SIM-VOLATILE model is a technology adoption model at the population level. The technology, in this model, is called Volatile Fatty Acid Platform (VFAP) and it is in the frame of the circular economy. The technology is considered an emerging technology and it is in the optimization phase. Through the adoption of VFAP, waste-treatment plants will be able to convert organic waste into high-end products rather than focusing on the production of biogas. Moreover, there are three adoption/investment scenarios as the technology enables the production of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA), single-cell oils (SCO), and polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA). However, due to differences in the processing related to the products, waste-treatment plants need to choose one adoption scenario.
In this simulation, there are several parameters and variables. Agents are heterogeneous waste-treatment plants that face the problem of circular economy technology adoption. Since the technology is emerging, the adoption decision is associated with high risks. In this regard, first, agents evaluate the economic feasibility of the emerging technology for each product (investment scenarios). Second, they will check on the trend of adoption in their social environment (i.e. local pressure for each scenario). Third, they combine these two economic and social assessments with an environmental assessment which is their environmental decision-value (i.e. their status on green technology). This combination gives the agent an overall adaptability fitness value (detailed for each scenario). If this value is above a certain threshold, agents may decide to adopt the emerging technology, which is ultimately depending on their predominant adoption probabilities and market gaps.
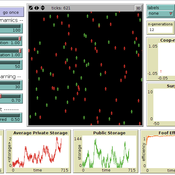
“Food for all” (FFD)
Andreas Angourakis José Manuel Galán Andrea L Balbo José Santos | Published Friday, April 25, 2014 | Last modified Monday, April 08, 2019“Food for all” (FFD) is an agent-based model designed to study the evolution of cooperation for food storage. Households face the social dilemma of whether to store food in a corporate stock or to keep it in a private stock.
Agent-Based Model for the Evolution of Ethnocentrism
Max Hartshorn | Published Saturday, March 24, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This is an implementation of an agent based model for the evolution of ethnocentrism. While based off a model published by Hammond and Axelrod (2006), the code has been modified to allow for a more fine-grained analysis of evolutionary dynamics.
E³-MAN. An Institutionally-guided multi-agent. Model for fair and efficient negotiation.
José luis bustelo | Published Monday, September 01, 2025Negotiation plays a fundamental role in shaping human societies, underpinning conflict resolution, institutional design, and economic coordination. This article introduces E³-MAN, a novel multi-agent model for negotiation that integrates individual utility maximization with fairness and institutional legitimacy. Unlike classical approaches grounded solely in game theory, our model incorporates Bayesian opponent modeling, transfer learning from past negotiation domains, and fallback institutional rules to resolve deadlocks. Agents interact in dynamic environments characterized by strategic heterogeneity and asymmetric information, negotiating over multidimensional issues under time constraints. Through extensive simulation experiments, we compare E³-MAN against the Nash bargaining solution and equal-split baselines using key performance metrics: utilitarian efficiency, Nash social welfare, Jain fairness index, Gini coefficient, and institutional compliance. Results show that E³-MAN achieves near-optimal efficiency while significantly improving distributive equity and agreement stability. A legal application simulating multilateral labor arbitration demonstrates that institutional default rules foster more balanced outcomes and increase negotiation success rates from 58% to 98%. By combining computational intelligence with normative constraints, this work contributes to the growing field of socially aware autonomous agents. It offers a virtual laboratory for exploring how simple institutional interventions can enhance justice, cooperation, and robustness in complex socio-legal systems.
COOPER - Flood impacts over Cooperative Winemaking Systems
David Nortes Martinez David Nortes-Martinez | Published Thursday, February 08, 2018 | Last modified Friday, March 22, 2019The model simulates flood damages and its propagation through a cooperative, productive, farming system, characterized as a star-type network, where all elements in the system are connected one to each other through a central element.
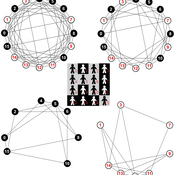
Mesoscopic Effects in an Agent-Based Bargaining Model in Regular Lattices
David Poza José Manuel Galán Ordax José Santos Adolfo López-Paredes | Published Thursday, February 02, 2017 | Last modified Wednesday, April 25, 2018We propose an agent-based model where a fixed finite population of tagged agents play iteratively the Nash demand game in a regular lattice. The model extends the bargaining model by Axtell, Epstein and Young.
Mitigating bioenergy-driven biodiversity decline: a modelling approach with the European brown hare
Volker Grimm Maria Langhammer | Published Wednesday, November 13, 2019 | Last modified Tuesday, November 24, 2020The model is designed to analyse the effects of mitigation measures on the European brown hare (Lepus europaeus), which is directly affected by ongoing land use change and has experienced widespread decline throughout Europe since the 1960s. As an input, we use two 4×4 km large model landscapes, which were generated by a landscape generator based on real field sizes and crop proportions and differed in average field size and crop composition. The crops grown annually are evaluated in terms of forage suitability, breeding suitability and crop richness for the hare. Six mitigation scenarios are implemented, defined by a 10 % increase in: (1) mixed silphie, (2) miscanthus, (3) grass-clover ley, (4) alfalfa, (5) set-aside, and (6) general crop richness. The model shows that that both landscape configuration and composition have a significant effect on hare population development, which responds particularly strongly to compositional changes.
Relational integration in schools through seating assignments
Károly Takács Marta Rado | Published Thursday, July 18, 2019We model interpersonal dynamics and study behavior in the classroom in the hypothetical case of a single teacher who defines students’ seating arrangements. The model incorporates the mechanisms of peer influence on study behavior, on attitude formation, and homophilous selection in order to depict the interrelated dynamics of networks, behavior, and attitudes. We compare various seating arrangement scenarios and observe how GPA distribution and level of prejudice changes over time.
Vulnerability of Cooperation Due to Limited Vision
Marco Janssen | Published Thursday, December 02, 2010 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This model describes the consequences of limited vision of agents in harvesting a common resource. We show the vulnerability of cooperation due to reduced visibility of the resource and other agents.
Displaying 10 of 53 results for "Jose María Cela" clear search