About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 490 results for "Tim M Daw" clear search
A discrete-time stochastic model with state-dependent transmission probabilities and multi-agent simulations focusing on possible risks that could materialize in the final phase of the epidemic.
A model of circular migration
Anna Klabunde | Published Wednesday, August 07, 2013 | Last modified Wednesday, February 17, 2016An empirically validated agent-based model of circular migration
Agent-based Modeling of Evolving Intergovernmental Networks
Sungho Lee | Published Thursday, January 29, 2009 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This agent-based model using ‘Blanche’ software provides policy-makers with a simulation-based demonstration illustrating how autonomous agents network and operate complementary systems in a decentral
Correlated random walk
Thibault Fronville | Published Friday, April 01, 2022 | Last modified Monday, April 25, 2022The first simple movement models used unbiased and uncorrelated random walks (RW). In such models of movement, the direction of the movement is totally independent of the previous movement direction. In other words, at each time step the direction, in which an individual is moving is completely random. This process is referred to as a Brownian motion.
On the other hand, in correlated random walks (CRW) the choice of the movement directions depends on the direction of the previous movement. At each time step, the movement direction has a tendency to point in the same direction as the previous one. This movement model fits well observational movement data for many animal species.
The presented agent based model simulated the movement of the agents as a correlated random walk (CRW). The turning angle at each time step follows the Von Mises distribution with a ϰ of 10. The closer ϰ gets to zero, the closer the Von Mises distribution becomes uniform. The larger ϰ gets, the more the Von Mises distribution approaches a normal distribution concentrated around the mean (0°).
This model is implemented in python and can be used as a building block for more complex agent based models that would rely on describing the movement of individuals with CRW.
Alternative scenarios of green consumption in Italy: an empirically grounded model.
Giangiacomo Bravo Elena Vallino Alessandro K Cerutti Maria Beatrice Pairotti | Published Thursday, March 28, 2013 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013We provide a full description of the model following the ODD protocol (Grimm et al. 2010) in the attached document. The model is developed in NetLogo 5.0 (Wilenski 1999).
FilterBubbles_in_Carley1991
Benoît Desmarchelier | Published Wednesday, May 21, 2025The model is an extension of: Carley K. (1991) “A theory of group stability”, American Sociological Review, vol. 56, pp. 331-354.
The original model from Carley (1991) works as follows:
- Agents know or ignore a series of knowledge facts;
- At each time step, each agent i choose a partner j to interact with at random, with a probability of choice proportional to the degree of knowledge facts they have in common.
- Agents interact synchronously. As such, interaction happens only if the partnert j is not already busy interacting with someone else.
…
Schwartz Human Values and the Economic Performance
Marcin Czupryna Bogumił Kamiński | Published Wednesday, November 29, 2023The purpose of the model is to provide an analogy for how the Schwartz values may influence the aggregated economic performance, as measured by: public goods provision, private goods provision and leisure time.
Scientific disagreements and the diagnosticity of evidence
Matteo Michelini | Published Wednesday, December 13, 2023The present model is an abstract ABM designed for theoretical exploration and hypotheses generation. Its main aim is to explore the relationship between disagreement over the diagnostic value of evidence and the formation of polarization in scientific communities.
The model represents a scientific community in which scientists aim to determine whether hypothesis H is true, and we assume that agents are in a world in which H is indeed true. To this end, scientists perform experiments, interpret data and exchange their views on how diagnostic of H the obtained evidence is. Based on how the scientists conduct the inquiry, the community may reach a correct consensus (i.e. a situation in which every scientist agrees that H is correct) or not.
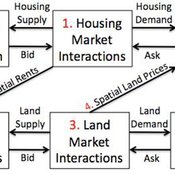
Coupled Housing and Land Markets (CHALMS)
Nicholas Magliocca Virginia Mcconnell Margaret Walls | Published Friday, November 02, 2012 | Last modified Monday, October 27, 2014CHALMS simulates housing and land market interactions between housing consumers, developers, and farmers in a growing ex-urban area.
Peer reviewed A Model of Global Diversity and Local Consensus in Status Beliefs
André Grow Andreas Flache Rafael Wittek | Published Wednesday, March 01, 2017 | Last modified Wednesday, October 25, 2017This model makes it possible to explore how network clustering and resistance to changing existing status beliefs might affect the spontaneous emergence and diffusion of such beliefs as described by status construction theory.
Displaying 10 of 490 results for "Tim M Daw" clear search