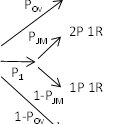
About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 206 results behavior clear search
Homophily-driven Network Evolution and Diffusion
Gönenç Yücel Mustafa Yavaş | Published Thursday, January 08, 2015The model is an experimental ground to study the impact of network structure on diffusion. It allows to construct a social network that already has some measurable level of homophily, and simulate a diffusion process over this social network.
Last Mile Commuter Behavior Model
Dean Massey Moira Zellner Yoram Shiftan Jonathan Levine Maria Arquero | Published Friday, November 07, 2014 | Last modified Friday, November 07, 2014We represent commuters and their preferences for transportation cost, time and safety. Agents assess their options via their preferences, their environment, and the modes available. The model has policy levers to test impact on last-mile problem.
This is the R code of the mathematical model that includes the decision making formulations for artificial agents. Plus, the code for graphical output is also added to the original code.
Parental choices, children's skills, and skill inequality: An agent-based model implemented in Python
Andrés Cardona | Published Thursday, October 30, 2014The model explores the emergence of inequality in cognitive and socio-emotional skills at the societal level within and across generations that results from differences in parental investment behavior during childhood and adolescence.
A stylized scale model to codesign with villagers an agent-based model of bushmeat hunting in the periphery of Korup National Park (Cameroon)
A Complex Model of Voter Turnout
Bruce Edmonds Laurence Lessard-Phillips Ed Fieldhouse | Published Monday, October 13, 2014 | Last modified Tuesday, August 18, 2015This is a complex “Data Integration Model”, following a “KIDS” rather than a “KISS” methodology - guided by the available evidence. It looks at the complex mix of social processes that may determine why people vote or not.
Peer reviewed Garbage can model Excel reconstruction
Smarzhevskiy Ivan | Published Tuesday, August 19, 2014 | Last modified Tuesday, July 30, 2019Reconstruction of the original code M. Cohen, J. March, and J. Olsen garbage can model, realized by means of Microsoft Office Excel 2010
ForagerNet3_Demography_V2
Andrew White | Published Thursday, February 13, 2014ForagerNet3_Demography_V2 is a non-spatial ABM for exploring hunter-gatherer demography. This version (developed from FN3D_V1) contains code for calculating the ratio of old to young adults (the “OY ratio”) in the living and dead populations.
How does the world population adapt its policies on energy when it is confronted with a climate change? This model combines a climate-economy model with adaptive agents.
This is the final version of the model. To simulate the normative dynamics we used the EmIL (EMergence In the Loop) Framework which was kindly provided by Ulf Lotzmann. http://cfpm.org/EMIL-D5.1.pdf
Displaying 10 of 206 results behavior clear search