About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 370 results for "Puqing Wang" clear search
Identity and meat eating behaviour
Jiaqi Ge | Published Thursday, September 29, 2022Using data from the British Social Attitude Survey, we develop an agent-based model to study the effect of social influence on the spread of meat-eating behaviour in the British population.
Peer reviewed Theoretical Model of Oak Persistence Under Competition and Herbivory
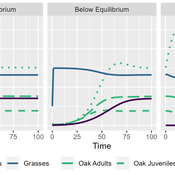
MV Eitzel Solera | Published Tuesday, October 25, 2022This model is intended to support oak tree management by representing the dynamics of oaks in multiple life stages and their competitors and consumers. This is implemented using a differential equation-based theoretical model representing three life stages of oaks: seedlings, juveniles, and adults. It includes the population dynamics of seedlings transitioning to juveniles, juveniles to adults, and adults producing new seedlings, as well as survival rates for each of the stages. It also includes a model of competition for light and water within seedlings and between seedlings and annual grasses. Finally, there is a predation term representing herbivores eating seedlings and grasses, using a Holling Type II (satiating) response with interference for predators and a death rate which depends on the resource extraction rate.
SimAdapt
François Rebaudo | Published Wednesday, August 29, 2012 | Last modified Monday, October 13, 2014SimAdapt: An individual-based genetic model for simulating landscape management impacts on populations
Community Forest Management with Monitoring and Sanctioning
Maya Lapp Colby Long | Published Wednesday, April 29, 2020 | Last modified Friday, July 23, 2021This NetLogo ABM builds on Elena Vallino’s model of Loggers using community-based natural resource management for a forest ecosystem. In it we introduce an alternative mechanism for Logger cheating and enforcement of CBNRM rules.
Homophily and Distance Depending Network Generation for Modelling Opinion Dynamics
Sascha Holzhauer | Published Wednesday, August 22, 2012 | Last modified Tuesday, June 18, 2013The model uses opinion dynamics to test a simple and ecient but empirically based approach for generating social networks in spatial agent-based models which explicitly takes into account restrictions and opportunities imposed by effects of baseline homophily and considers the probability of links that depends on geographical distance between potential partners.
Netlogo model ` Effect of Network Homophily and Partisanship on Social Media to “Oil Spill” Polarizations’
takuya nagura | Published Saturday, September 13, 2025This model was utilized for the simulation in the paper titled Effect of Network Homophily and Partisanship on Social Media to “Oil Spill” Polarizations. It allows you to examine whether oil spill polarization occurs through people’s communication under various conditions.
・Choose the network construction conditions you’d like to examine from the “rewire-style” chooser box.
・Select the desired strength of partisanship from the “partisanlevel” chooser box. You can also set the strength manually in the code tab.
・You can set the number of dynamic topics using the “number-of-topics” slider.
・Use the “divers-of-opinion” slider to set the number of preference types for each dynamic topic.
…
Stationarity Test
Jakob Grazzini | Published Monday, November 29, 2010 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This is a stationarity test, it tests whether a given moment is constant during the time series (null hypothesis). The Wald Wolfowitz nonparametric fitness test is applied to time series.
Harvesting daisies in Daisyworld
Marco Janssen | Published Saturday, July 22, 2017Comparing impact of alternative behavioral theories in a simple social-ecological system.
Network structures tutorial
Tom Brughmans | Published Sunday, September 30, 2018 | Last modified Tuesday, October 02, 2018A draft model with some useful code for creating different network structures using the Netlogo NW extension. This model is used for the following tutorial:
Brughmans, T. (2018). Network structures and assembling code in Netlogo, Tutorial, https://archaeologicalnetworks.wordpress.com/resources/#structures .
IDEAL
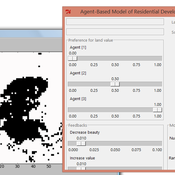
Arika Ligmann-Zielinska | Published Thursday, August 07, 2014IDEAL: Agent-Based Model of Residential Land Use Change where the choice of new residential development in based on the Ideal-point decision rule.
Displaying 10 of 370 results for "Puqing Wang" clear search