About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 208 results for "Marc Choisy" clear search
Walk Away in groups
Athena Aktipis | Published Thursday, March 17, 2016This NetLogo model implements the Walk Away strategy in a spatial public goods game, where individuals have the ability to leave groups with insufficient levels of cooperation.
Agent-based model of risk behavior in adolescence
N Schuhmacher P Van Geert L Ballato | Published Monday, June 24, 2013 | Last modified Monday, April 08, 2019The computer model simulates the development of a social network (i.e. formation of friendships and cliques), the (dyadic) interactions between pupils and the development of similarities and differences in their behavioral profiles.
A Consumer in the Jungle of Product Differentiation
Alessandro Pluchino Andrea Rapisarda Alessio Emanuele Biondo Alfio Giarlotta | Published Tuesday, December 22, 2015Building upon the distance-based Hotelling’s differentiation idea, we describe the behavioral experience of several prototypes of consumers, who walk a hypothetical cognitive path in an attempt to maximize their satisfaction.
The Agent-Based Model of the Closed Market( similar to Stock Market) with One Commodity and with careful and risky mechanisms
Mark Voronovitsky | Published Sunday, March 15, 2015 | Last modified Sunday, March 22, 2015The model of market of one commodity , in which there are in each moment of time the same quantity and the same quantity of money was formulated and researched in this text. We also study this system as a game of automata.
Linear Threshold
Kaushik Sarkar | Published Saturday, November 03, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013NetLogo implementation of Linear Threshold model of influence propagation.
The effect of error on cultural transmission
Claudine Gravel-Miguel | Published Thursday, November 01, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This is the replication of the experiment performed by Eerkens and Lipo (2005) to look at the effect of copying errors when specific traits are transferred from an individual to another.
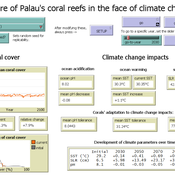
Development of coral reefs under climate change impacts and adaptation options
Nina Preußler | Published Friday, May 30, 2025This NetLogo model simulates how coral reefs around the islands of Palau would develop under different emission scenarios and with selected adaptation strategies. Reef health is indicated by coral cover (%) and is affected by four major climate change impacts: increasing sea surface temperature, sea level rise, ocean acidification, and more intense typhoons. The model differentiates between inner and outer reefs, with the former naturally adapted to warmer, more acidic waters. The simulation includes bleaching events and possible recovery. In addition, the user can choose between different coral transplantation strategies as well as regulate natural thermal adaptation rates.
Can ethnic tolerance curb self-reinforcing school segregation? A theoretical Agent Based Model
Lucas Sage Andreas Flache | Published Monday, August 10, 2020Schelling and Sakoda prominently proposed computational models suggesting that strong ethnic residential segregation can be the unintended outcome of a self-reinforcing dynamic driven by choices of individuals with rather tolerant ethnic preferences. There are only few attempts to apply this view to school choice, another important arena in which ethnic segregation occurs. In the current paper, we explore with an agent-based theoretical model similar to those proposed for residential segregation, how ethnic tolerance among parents can affect the level of school segregation. More specifically, we ask whether and under which conditions school segregation could be reduced if more parents hold tolerant ethnic preferences. We move beyond earlier models of school segregation in three ways. First, we model individual school choices using a random utility discrete choice approach. Second, we vary the pattern of ethnic segregation in the residential context of school choices systematically, comparing residential maps in which segregation is unrelated to parents’ level of tolerance to residential maps reflecting their ethnic preferences. Third, we introduce heterogeneity in tolerance levels among parents belonging to the same group. Our simulation experiments suggest that ethnic school segregation can be a very robust phenomenon, occurring even when about half of the population prefers mixed to segregated schools. However, we also identify a “sweet spot” in the parameter space in which a larger proportion of tolerant parents makes the biggest difference. This is the case when parents have moderate preferences for nearby schools and there is only little residential segregation. Further experiments are presented that unravel the underlying mechanisms.
The role of spatial foresight in models of hominin dispersal
Colin Wren | Published Monday, February 24, 2014 | Last modified Monday, July 14, 2014The natural selection of foresight, an accuracy at assess the environment, under degrees of environmental heterogeneity. The model is designed to connect local scale mobility, from foraging, with the global scale phenomenon of population dispersal.
Linear recruitment leads to allocation and flexibility in collective foraging by ants
Takao Sasaki Zachary Joseph Shaffer Stephen Pratt | Published Thursday, July 11, 2013 | Last modified Thursday, September 05, 2013Ants in the genus Temnothorax use tandem runs (rather than pheromone trails) to recruit to food sources. This model explores the collective consequences of this linear recruitment (as opposed to highly nonlinear pheromone trails).
Displaying 10 of 208 results for "Marc Choisy" clear search