About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 443 results simulation clear search
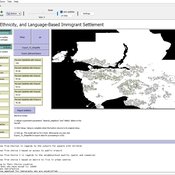
Geospatial Agent-Based Model of Immigrant Settlement Dynamics in Metro Vancouver
Liliana Perez Navid Mahdizadeh Gharakhanlou Maryam Yousefi | Published Wednesday, December 03, 2025This agent-based model simulates how new immigrant households choose where to live in Metro Vancouver under the origins diversity scenario. The model begins with 16,000 household agents, reflecting an expected annual population increase of about 42,500 people based on an average household size of 2.56. Each agent is assigned four characteristics: one of ten origin categories, income level (adjusted using NOC data and recent immigrant earnings), likelihood of having children, and preferred mode of commuting. The ten origin groups are drawn from Census patterns, including six subgroups within the broader Asian category (China, India, the Philippines, Iran, South Korea, and Other Asian countries) and two categories for immigrants from the Americas. This refined classification better captures the diversity of newcomers arriving in the region.
Structural Violence and Neurobiological Adaptation: Modeling the Trajectory of Youth Outside of Care
masterpiece33330-prog | Published Thursday, November 27, 2025This study presents a System Dynamics (SD) model that explores the “trajectories of homelessness” among youth outside of the formal care system. Unlike traditional approaches that view runaway behavior as a discrete choice, this model reinterprets it as a neurobiological adaptation to chronic resource deprivation and systemic neglect.
The model incorporates key mechanisms such as ‘Allostatic Load’ accumulation, ‘PFC-Amygdala Switching’, and the ‘Iatrogenic Effects’ of shelter policies. It utilizes Monte Carlo simulations to demonstrate how structural factors create a “probabilistic vulnerability,” trapping youth in cycles of survival crime and isolation regardless of individual resilience.
The uploaded code includes a Python implementation of the model to ensure reproducibility of the stochastic analysis presented in the paper.
Agent-based Modelling of Unsustainable and Sustainable Norms Under Resource Constraints
Fachrizal Sinaga Adrian Thomas Sufyan Fawwad | Published Monday, November 24, 2025This model explores the coupled dynamics of social norm diffusion and finite resource depletion. Extending the “Affordance Landscape” framework by Kaaronen & Strelkovskii (2020), this simulation investigates how resource scarcity and regeneration rates influence the adoption of pro-environmental behaviours.
The model addresses the gap by linking behavioural norms to a depleting common-pool resource. It tests whether sustainable norms can diffuse rapidly enough to prevent ecological collapse and identifies “tipping points” where resource scarcity acts as a driver for behavioural change.
Behavioural model
Aulia Imania Sukma | Published Friday, November 07, 2025This repository serves as a design proof for agent-based modeling simulation in heat adaptation behavior. This model was developed as part of the UrbanAir project theme. This repository will be kept updated in the four-year timeline (2025 until 2029).
Peer reviewed The effect of homophily on co-offending outcomes
Ruslan Klymentiev Christophe Vandeviver Luis E. C. Rocha | Published Friday, September 26, 2025This Agent-Based Model is designed to simulate how similarity-based partner selection (homophily) shapes the formation of co-offending networks and the diffusion of skills within those networks. Its purpose is to isolate and test the effects of offenders’ preference for similar partners on network structure and information flow, under controlled conditions.
In the model, offenders are represented as agents with an individual attribute and a set of skills. At each time step, agents attempt to select partners based on similarity preference. When two agents mutually select each other, they commit a co-offense, forming a tie and exchanging a skill. The model tracks the evolution of network properties (e.g., density, clustering, and tie strength) as well as the spread of skills over time.
This simple and theoretical model does not aim to produce precise empirical predictions but rather to generate insights and test hypotheses about the trade-off between network stability and information diffusion. It provides a flexible framework for exploring how changes in partner selection preferences may lead to differences in criminal network dynamics. Although the model was developed to simulate offenders’ interactions, in principle, it could be applied to other social processes involving social learning and skills exchange.
…
Netlogo model ` Effect of Network Homophily and Partisanship on Social Media to “Oil Spill” Polarizations’
takuya nagura | Published Saturday, September 13, 2025This model was utilized for the simulation in the paper titled Effect of Network Homophily and Partisanship on Social Media to “Oil Spill” Polarizations. It allows you to examine whether oil spill polarization occurs through people’s communication under various conditions.
・Choose the network construction conditions you’d like to examine from the “rewire-style” chooser box.
・Select the desired strength of partisanship from the “partisanlevel” chooser box. You can also set the strength manually in the code tab.
・You can set the number of dynamic topics using the “number-of-topics” slider.
・Use the “divers-of-opinion” slider to set the number of preference types for each dynamic topic.
…
Peer reviewed E³-MAN. An Institutionally-guided multi-agent. Model for fair and efficient negotiation.
José luis bustelo | Published Monday, September 01, 2025Negotiation plays a fundamental role in shaping human societies, underpinning conflict resolution, institutional design, and economic coordination. This article introduces E³-MAN, a novel multi-agent model for negotiation that integrates individual utility maximization with fairness and institutional legitimacy. Unlike classical approaches grounded solely in game theory, our model incorporates Bayesian opponent modeling, transfer learning from past negotiation domains, and fallback institutional rules to resolve deadlocks. Agents interact in dynamic environments characterized by strategic heterogeneity and asymmetric information, negotiating over multidimensional issues under time constraints. Through extensive simulation experiments, we compare E³-MAN against the Nash bargaining solution and equal-split baselines using key performance metrics: utilitarian efficiency, Nash social welfare, Jain fairness index, Gini coefficient, and institutional compliance. Results show that E³-MAN achieves near-optimal efficiency while significantly improving distributive equity and agreement stability. A legal application simulating multilateral labor arbitration demonstrates that institutional default rules foster more balanced outcomes and increase negotiation success rates from 58% to 98%. By combining computational intelligence with normative constraints, this work contributes to the growing field of socially aware autonomous agents. It offers a virtual laboratory for exploring how simple institutional interventions can enhance justice, cooperation, and robustness in complex socio-legal systems.
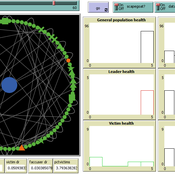
An agent-based model of scapegoating
Carlos Paes | Published Thursday, August 28, 2025 | Last modified Thursday, August 28, 2025This agent-based model investigates scapegoating as a social mechanism of crisis management. Inspired by René Girard’s mimetic theory, it simulates how individual tension accumulates and spreads across a small-world network. When tension exceeds certain thresholds, leaders emerge and accuse marginalized agents, who may attempt to transfer blame to substitutes. If scapegoating occurs, collective tension decreases, but victims become isolated while leaders consolidate temporary authority. This simulation provides a conceptual and methodological framework for exploring how collective blame, crisis contagion, and leadership paradoxes emerge in complex networks. It can also be extended with empirical data, such as social media dynamics of online harassment and virtual lynching, offering potential applications for both theoretical research and practical crisis monitoring.
LogoClim: WorldClim in NetLogo
Daniel Vartanian Leandro Garcia Aline Martins de Carvalho Aline | Published Thursday, July 03, 2025 | Last modified Tuesday, September 16, 2025LogoClim is a NetLogo model for simulating and visualizing global climate conditions. It allows researchers to integrate high-resolution climate data into agent-based models, supporting reproducible research in ecology, agriculture, environmental sciences, and other fields that rely on climate data.
The model utilizes raster data to represent climate variables such as temperature and precipitation over time. It incorporates historical data (1951-2024) and future climate projections (2021-2100) derived from global climate models under various Shared Socioeconomic Pathways (SSPs, O’Neill et al., 2017). All climate inputs come from WorldClim 2.1, a widely used source of high-resolution, interpolated climate datasets based on weather station observations worldwide (Fick & Hijmans, 2017).
LogoClim follows the FAIR Principles for Research Software (Barker et al., 2022) and is openly available on the CoMSES Network and GitHub. See the Logônia model for an example of its integration into a full NetLogo simulation.
Peer reviewed ACross (Academic Collaboration, Research, Output, and System Simulation)
Wenhan Feng Bayi Li | Published Saturday, June 28, 2025The primary purpose of this model is to explain the dynamic processes within university-centered collaboration networks, with a particular focus on the complex transformation of academic knowledge into practical projects. Based on investigations of actual research projects and a thorough literature review, the model integrates multiple drivers and influencing factors to explore how these factors affect the formation and evolution of collaboration networks under different parameter scenarios. The model places special emphasis on the impact of disciplinary attributes, knowledge exchange, and interdisciplinary collaboration on the dynamics of collaboration networks, as well as the complex mechanisms of network structure, system efficiency, and interdisciplinary interactions during project formation.
Specifically, the model aims to:
- Simulate how university research departments drive the formation of research projects through knowledge creation.
- Investigate how the dynamics of collaboration networks influence the transformation of innovative hypotheses into matured projects.
- Examine the critical roles of knowledge exchange and interdisciplinary collaboration in knowledge production and project formation.
- Provide both quantitative and qualitative insights into the interactions among academia, industry, and project outputs.
Displaying 10 of 443 results simulation clear search