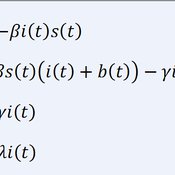About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 212 results population clear search
Foundress dilemma model
Marco Janssen Takao Sasaki Zachary Joseph Shaffer Stephen Pratt Brian Haney Jennifer Fewell | Published Thursday, July 28, 2016A haystack-style model of group selection to capture the essential features of colony foundation for queens of the ant based on observation of the ant Pogonomyrmex californicus.
A model to explore the link between the gender-gap reversal in education and relative divorce risks
Jan Van Bavel Christine Schnor André Grow | Published Thursday, June 30, 2016 | Last modified Wednesday, September 13, 2017This model explores a social mechanism that links the reversal of the gender gap in education with changing patterns in relative divorce risks in 12 European countries.
Opinions on contested energy infrastructures
Annalisa Stefanelli | Published Thursday, June 23, 2016This ABM simulates opinions on a topic (originally contested infrastructures) through the interactions between paired agents and based on the sociopsychological assumptions of social judgment theory (SJT; Sherif & Hovland, 1961).
Central-place forager mobility and cultural diversity
Luke Premo | Published Wednesday, May 18, 2016This spatially explicit agent-based model addresses how effective foraging radius (r_e) affects the effective size–and thus the equilibrium cultural diversity–of a structured population composed of central-place foraging groups.
Effective population size and cultural evolution
Luke Premo | Published Tuesday, May 17, 2016This model illustrates how the effective population size and the rate of change in mean skill level of a cultural trait are affected by the presence of natural selection and/or the cultural transmission mechanism by which it is passed.
Communication and social change in space and time
Sebastian Kluesener Francesco Scalone Martin Dribe | Published Tuesday, May 17, 2016 | Last modified Friday, October 13, 2017This agent-based model simulates the diffusion of a social change process stratified by social class in space and time which is solely driven social and spatial variation in communication links.
An Agent-based Model of Collective Self-organisation in Irrigation Management
Hang Xiong Jingjing Cai | Published Wednesday, April 06, 2016This model simulates how collective self-organisation among individuals that manage irrigation resource collectively.
Walk Away in groups
Athena Aktipis | Published Thursday, March 17, 2016This NetLogo model implements the Walk Away strategy in a spatial public goods game, where individuals have the ability to leave groups with insufficient levels of cooperation.
Product Diffusion Model in an Advance Selling Strategy
Peng Shao | Published Tuesday, March 15, 2016 | Last modified Tuesday, March 15, 2016the model can be used to describe the product diffusion in an Advance Selling Strategy. this model takes into account the consumers product adoption, and describe consumer’s online behavior based on four states.
Relative Agreement Model and Network Structure
Spiro Maroulis David Adelberg | Published Friday, January 29, 2016This adaptation of the Relative Agreement model of opinion dynamics (Deffuant et al. 2002) extends the Meadows and Cliff (2012) implementation of this model in a manner that explores the effect of the network structure among the agents.
Displaying 10 of 212 results population clear search