About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers at all levels engage in the establishment and adoption of community standards and good practices for developing and sharing computational models. Model authors can freely publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library alongside narrative documentation, open science metadata, and other emerging open science norms that facilitate software citation, reproducibility, interoperability, and reuse. Model authors can also request peer review of their computational models to receive a DOI.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with additional detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 756 results agent clear search
Salzburg Bicycle model
Gudrun Wallentin | Published Saturday, October 29, 2016An ABM to simulate the spatio-temporal distribution of cyclists across the road network of the city of Salzburg.
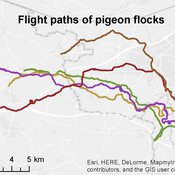
Homing pigeon model
Gudrun Wallentin | Published Saturday, October 29, 2016This model represents the flight paths of a flock of homing pigeons according to their flocking-, orientation- and leadership behaviour.
Hybrid fish-plankton model
Gudrun Wallentin Christian Neuwirth | Published Friday, October 28, 2016 | Last modified Sunday, January 29, 2017A hybrid predator-prey model of fish and plankton that switches dynamically between ABM and SD representations. It contains 6 related structural designs of the same model.
PA/C model with affinity
N. Leticia Abrica-Jacinto Evguenii Kurmyshev Héctor Juárez | Published Thursday, October 27, 2016We expose RA agent-based model of the opinion and tolerance dynamics in artificial societies. The formal mathematical model is based on the ideas of Social Influence, Social Judgment, and Social Identity theories.
Peer reviewed Simulating the Economic Impact of Boko Haram on a Cameroonian Floodplain
Mark Moritz Nathaniel Henry Sarah Laborde | Published Saturday, October 22, 2016 | Last modified Wednesday, June 07, 2017This model examines the potential impact of market collapse on the economy and demography of fishing households in the Logone Floodplain, Cameroon.
Adoption as a social marker
Paul Smaldino | Published Monday, October 17, 2016A model of innovation diffusion in a structured population with two groups who are averse to adopting a produce popular with the outgroup.
Eliminating hepatitis C virus as a public health threat among HIV-positive men who have sex with men
Nick Scott Mark Stoove David P Wilson Olivia Keiser Carol El-Hayek Joseph Doyle Margaret Hellard | Published Wednesday, October 12, 2016 | Last modified Sunday, December 16, 2018We compare three model estimates for the time and treatment requirements to eliminate HCV among HIV-positive MSM in Victoria, Australia: a compartmental model; an ABM parametrized by surveillance data; and an ABM with a more heterogeneous population.
Institutional change
Abigail Sullivan | Published Friday, October 07, 2016 | Last modified Sunday, December 02, 2018This model builds on another model in this library (“diffusion of culture”).
Urban-Dynamics-2017
Hideyuki Nagai Setsuya Kurahashi | Published Thursday, October 06, 2016 | Last modified Thursday, October 06, 2016This model is designed for the paper of “Bustle Changes the City - Facility for Stopping off and Modeling Urban Dynamics -“. And all experimental results in the paper were implemented in this model.
Multi Asset Variable Network Stock Market Model
Matthew Oldham | Published Monday, September 12, 2016 | Last modified Tuesday, October 10, 2017An artifcal stock market model that allows users to vary the number of risky assets as well as the network topology that investors forms in an attempt to understand the dynamics of the market.
Displaying 10 of 756 results agent clear search