About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers at all levels engage in the establishment and adoption of community standards and good practices for developing and sharing computational models. Model authors can freely publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library alongside narrative documentation, open science metadata, and other emerging open science norms that facilitate software citation, reproducibility, interoperability, and reuse. Model authors can also request peer review of their computational models to receive a DOI.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with additional detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1086 results for "Clint A Penick" clear search
Sociodynamica in a Browser
Klaus Jaffe | Published Saturday, December 24, 2016Sociodynamica simulates the emergence of cooperation and of economic interactions, showing the synergy achieved by division of labor, the working of shame, and a number of other features that mold the evolution of social cooperation.
Consumats on a network
Marco Janssen | Published Tuesday, January 14, 2020 | Last modified Tuesday, May 30, 2023Consumer agents make choices which products to choose using the consumat approach. In this approach agents will make choices using deliberation, repetition, imitation or social comparison dependent on the level of need satisfaction and uncertainty.
The model is discussed in Introduction to Agent-Based Modeling by Marco Janssen. For more information see https://intro2abm.com/
A-KinGDom: A Kinship, Grooming and Dominance Model for Primate Societies
Ruth Dolado Francesc S Beltran Vicenc Quera | Published Thursday, July 11, 2013 | Last modified Wednesday, July 17, 2013A-KinGDom simulates the emergence of the social structure in a group of non-human primates. The model includes dominance and affiliative interactions which allow us to define four different attack and affiliative strategies.
Modeling information Asymmetries in Tourism
Jacopo A. Baggio Rodolfo Baggio | Published Monday, January 09, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013A very simple model elaborated to explore what may happens when buyers (travelers) have more information than sellers (tourist destinations)
Success bias imitation increases the probability of effectively dealing with ecological disturbances
Jacopo A. Baggio Vicken Hillis | Published Thursday, April 13, 2017 | Last modified Thursday, August 02, 2018This model aims to investigate how different type of learning (social system) and disturbance specific attributes (ecological system) influence adoption of treatment strategies to treat the effects of ecological disturbances.
Managing ecological disturbances: Learning and the structure of social-ecological networks
Jacopo A. Baggio Vicken Hillis | Published Friday, March 03, 2017 | Last modified Thursday, August 02, 2018The aim of this model is to explore and understand the factors driving adoption of treatment strategies for ecological disturbances, considering payoff signals, learning strategies and social-ecological network structure
Two agent-based models of cooperation in dynamic groups and fixed social networks
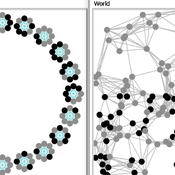
Carlos A. de Matos Fernandes | Published Thursday, January 20, 2022Both models simulate n-person prisoner dilemma in groups (left figure) where agents decide to C/D – using a stochastic threshold algorithm with reinforcement learning components. We model fixed (single group ABM) and dynamic groups (bad-barrels ABM). The purpose of the bad-barrels model is to assess the impact of information during meritocratic matching. In the bad-barrels model, we incorporated a multidimensional structure in which agents are also embedded in a social network (2-person PD). We modeled a random and homophilous network via a random spatial graph algorithm (right figure).
A Double-Auction Equity Market For a Single Firm with AR1 Earnings
Eric Weisbrod | Published Monday, December 13, 2010 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This is a final project for the class AML 591 at Arizona State University. I have done a small amount of bug-checking, but overall the project represents only a half of a semester’s work, so proceed w
ManPraSim: A Management Practice Simulation
peer-olaf_siebers | Published Wednesday, February 23, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This simulation model is associated with the journal paper “A First Approach on Modelling Staff Proactiveness in Retail Simulation Models” to appear in the Journal of Artificial Societies and Social Simulation 14 (2) 2. The authors are Peer-Olaf Siebers ([email protected]) and Uwe Aickelin ([email protected]).
A model of circular migration
Anna Klabunde | Published Wednesday, August 07, 2013 | Last modified Wednesday, February 17, 2016An empirically validated agent-based model of circular migration
Displaying 10 of 1086 results for "Clint A Penick" clear search