Evolution of Cooperation in Asymmetric Commons Dilemmas (1.0.0)
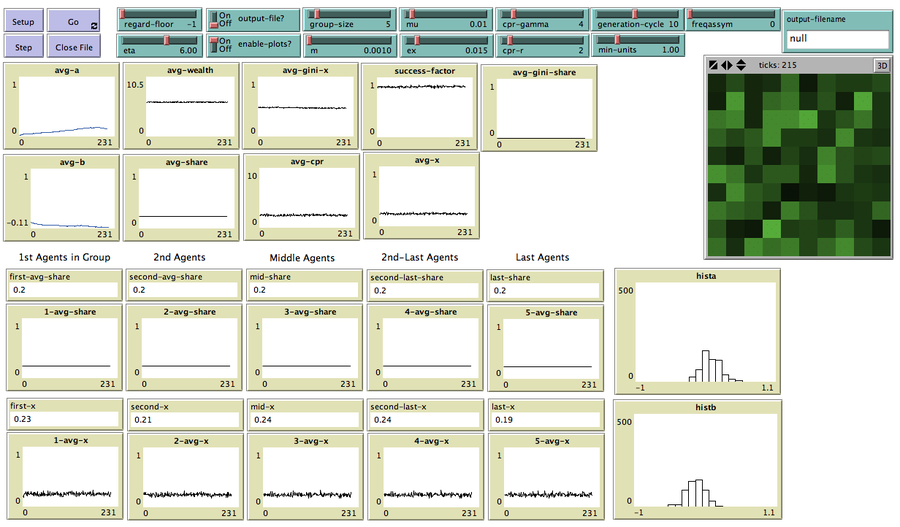
This model can be used to explore under which conditions agents behave as observed in field experiments on irrigation games. In irrigation games participants have different levels of access to the resource. This asymmetry causes that agents downstream reduce investment in the common infrastructure if they do not get a large enough share of the common pool. Participants balance efficiency and equity. When do agents evolve who do the same?
Release Notes
Associated Publications
Janssen, M.A. and N.D. Rollins (2012). Evolution of cooperation in asymmetric commons dilemmas. Journal of Economic Behavior and Organization, 81: 220-229
This release is out-of-date. The latest version is
1.1.0
Evolution of Cooperation in Asymmetric Commons Dilemmas 1.0.0
Submitted by
Marco Janssen
Published Aug 20, 2010
Last modified Dec 05, 2024
This model can be used to explore under which conditions agents behave as observed in field experiments on irrigation games. In irrigation games participants have different levels of access to the resource. This asymmetry causes that agents downstream reduce investment in the common infrastructure if they do not get a large enough share of the common pool. Participants balance efficiency and equity. When do agents evolve who do the same?