About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers at all levels engage in the establishment and adoption of community standards and good practices for developing and sharing computational models. Model authors can freely publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library alongside narrative documentation, open science metadata, and other emerging open science norms that facilitate software citation, reproducibility, interoperability, and reuse. Model authors can also request peer review of their computational models to receive a DOI.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with additional detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 4 of 4 results diet breadth model clear search
An age and/or gender-based division of labor during the Last Glacial Maximum in Iberia through rabbit hunting
Liliana Perez Samuel Seuru Ariane Burke | Published Thursday, February 29, 2024Many archaeological assemblages from the Iberian Peninsula dated to the Last Glacial Maximum contain large quantities of European rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus) remains with an anthropic origin. Ethnographic and historic studies report that rabbits may be mass-collected through warren-based harvesting involving the collaborative participation of several persons.
We propose and implement an Agent-Based Model grounded in the Optimal Foraging Theory and the Diet Breadth Model to examine how different warren-based hunting strategies influence the resulting human diets.
…
An age and/or gender-based division of labor during the Last Glacial Maximum in Iberia through rabbit hunting
Liliana Perez Samuel Seuru Ariane Burke | Published Friday, July 07, 2023Many archaeological assemblages from the Iberian Peninsula dated to the Last Glacial Maximum contain large quantities of European rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus) remains with an anthropic origin. Ethnographic and historic studies report that rabbits may be mass-collected through warren-based harvesting involving the collaborative participation of several persons.
We propose and implement an Agent-Based Model grounded in the Optimal Foraging Theory and the Diet Breadth Model to examine how different warren-based hunting strategies influence the resulting human diets.
Particularly, this model is developed to test the following hypothesis: What if an age and/or gender-based division of labor was adopted, in which adult men focus on large prey hunting, and women, elders and children exploit warrens?
…
PalaeoDiet : Rabbit hunting during the Upper Palaeolithic
Liliana Perez Samuel Seuru Ariane Burke | Published Thursday, October 06, 2022Zooarchaeological evidences indicate that rabbit hunting became prevalent during the Upper Palaeolithic in the Iberian Peninsula.
The purpose of the ABM is to test if warren hunting using nets as a collective strategy can explain the introduction of rabbits in the human diet in the Iberian Peninsula during this period. It is analyzed whether this hunting strategy has an impact on human diet breadth by affecting the relative abundance of other main taxa in the dietary spectrum.
Model validity is measured by comparing simulated diet breadth to the observed diet breadth in the zooarchaeological record.
The agent-based model is explicitly grounded on the Diet Breadth Model (DBM), from the Optimal Foraging Theory (OFT).
…
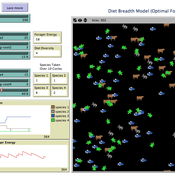
Diet breadth model from Optimal Foraging Theory (Human Behavioral Ecology)
C Michael Barton | Published Wednesday, November 26, 2008 | Last modified Thursday, March 12, 2015Diet breadth is a classic optimal foraging theory (OFT) model from human behavioral ecology (HBE). Different resources, ranked according to their food value and processing costs, are distributed in th