About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 318 results for "Shu-Heng Chen" clear search
An agent-based model of building occupant behavior during load shedding
Handi Chandra Putra | Published Thursday, May 21, 2020Load shedding enjoys increasing popularity as a way to reduce power consumption in buildings during hours of peak demand on the electricity grid. This practice has well known cost saving and reliability benefits for the grid, and the contracts utilities sign with their “interruptible” customers often pass on substantial electricity cost savings to participants. Less well-studied are the impacts of load shedding on building occupants, hence this study investigates those impacts on occupant comfort and adaptive behaviors. It documents experience in two office buildings located near Philadelphia (USA) that vary in terms of controllability and the set of adaptive actions available to occupants. An agent-based model (ABM) framework generalizes the case-study insights in a “what-if” format to support operational decision making by building managers and tenants. The framework, implemented in EnergyPlus and NetLogo, simulates occupants that have heterogeneous
thermal and lighting preferences. The simulated occupants pursue local adaptive actions such as adjusting clothing or using portable fans when central building controls are not responsive, and experience organizational constraints, including a corporate dress code and miscommunication with building managers. The model predicts occupant decisions to act fairly well but has limited ability to predict which specific adaptive actions occupants will select.
Peer reviewed Share: bottom-up disaster information management
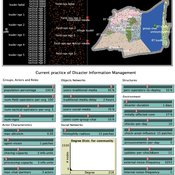
Vittorio Nespeca Tina Comes Frances Brazier | Published Monday, December 05, 2022This model is intended to study the way information is collectively managed (i.e. shared, collected, processed, and stored) in a system and how it performs during a crisis or disaster. Performance is assessed in terms of the system’s ability to provide the information needed to the actors who need it when they need it. There are two main types of actors in the simulation, namely communities and professional responders. Their ability to exchange information is crucial to improve the system’s performance as each of them has direct access to only part of the information they need.
In a nutshell, the following occurs during a simulation. Due to a disaster, a series of randomly occurring disruptive events takes place. The actors in the simulation need to keep track of such events. Specifically, each event generates information needs for the different actors, which increases the information gaps (i.e. the “piles” of unaddressed information needs). In order to reduce the information gaps, the actors need to “discover” the pieces of information they need. The desired behavior or performance of the system is to keep the information gaps as low as possible, which is to address as many information needs as possible as they occur.
U-TRANS Modelling Urban Transition with Coupled Housing and Labour Markets
Bernardo Furtado Jiaqi Ge | Published Monday, July 31, 2023We develop an agent-based model (U-TRANS) to simulate the transition of an abstract city under an industrial revolution. By coupling the labour and housing markets, we propose a holistic framework that incorporates the key interacting factors and micro processes during the transition. Using U-TRANS, we look at five urban transition scenarios: collapse, weak recovery, transition, enhanced training and global recruit, and find the model is able to generate patterns observed in the real world. For example, We find that poor neighbourhoods benefit the most from growth in the new industry, whereas the rich neighbourhoods do better than the rest when the growth is slow or the situation deteriorates. We also find a (subtle) trade-off between growth and equality. The strategy to recruit a large number of skilled workers globally will lead to higher growth in GDP, population and human capital, but it will also entail higher inequality and market volatility, and potentially create a divide between the local and international workers. The holistic framework developed in this paper will help us better understand urban transition and detect early signals in the process. It can also be used as a test-bed for policy and growth strategies to help a city during a major economic and technological revolution.
Leviathan group model and its approximation
Thibaut Roubin Guillaume Deffuant | Published Tuesday, July 26, 2022The model is based on the influence function of the Leviathan model (Deffuant, Carletti, Huet 2013 and Huet and Deffuant 2017) with the addition of group idenetity. We aim at better explaining some patterns generated by this model, using a derived mathematical approximation of the evolution of the opinions averaged.
We consider agents having an opinion/esteem about each other and about themselves. During dyadic meetings, agents change their respective opinion about each other, and possibly about other agents they gossip about, with a noisy perception of the opinions of their interlocutor. Highly valued agents are more influential in such encounters. Moreover, each agent belongs to a single group and the opinions within the group are attracted to their average.
We show that a group hierarchy can emerges from this model, and that the inequality of reputations among groups have a negative effect on the opinions about the groups of low status. The mathematical analysis of the opinion dynamic shows that the lower the status of the group, the more detrimental the interactions with the agents of other groups are for the opinions about this group, especially when gossip is activated. However, the interactions between agents of the same group tend to have a positive effect on the opinions about this group.
A preliminary extension of the Hemelrijk 1996 model of reciprocal behavior to include feeding
Sean Barton | Published Monday, December 13, 2010 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013A more complete description of the model can be found in Appendix I as an ODD protocol. This model is an expansion of the Hemelrijk (1996) that was expanded to include a simple food seeking behavior.
SONG - Simulation of Network Growth
D Levinson | Published Monday, August 29, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013SONG is a simulator designed for simulating the process of transportation network growth.
Food Safety Inspection Model - Random Strategy
Sara Mcphee-Knowles | Published Wednesday, March 05, 2014 | Last modified Monday, April 08, 2019The Inspection Model represents a basic food safety system where inspectors, consumers and stores interact. The purpose of the model is to provide insight into an optimal level of inspectors in a food system by comparing three search strategies.
Food Safety Inspection Model - Stores Signal with Errors
Sara Mcphee-Knowles | Published Wednesday, March 05, 2014 | Last modified Monday, April 08, 2019The Inspection Model represents a basic food safety system where inspectors, consumers and stores interact. The purpose of the model is to provide insight into an optimal level of inspectors in a food system by comparing three search strategies.
Food Safety Inspection Model - Stores Signal
Sara Mcphee-Knowles | Published Wednesday, March 05, 2014 | Last modified Monday, August 26, 2019The Inspection Model represents a basic food safety system where inspectors, consumers and stores interact. The purpose of the model is to provide insight into an optimal level of inspectors in a food system by comparing three search strategies.
Demographic microsimulation for individuals and couples
Sabine Zinn | Published Wednesday, January 14, 2015The simulation model conducts fine-grained population projection by specifying life course dynamics of individuals and couples by means of traditional demographic microsimulation and by using agent-based modeling for mate matching.
Displaying 10 of 318 results for "Shu-Heng Chen" clear search