Garry Sotnik
Affiliations Professional homepagehttps://profiles.stanford.edu/garry-sotnik
ORCID more infohttps://orcid.org/0000-0002-2422-1110
GitHub more info
Garry Sotnik is a lecturer at the Stanford Doerr School of Sustainability, teaching human adaptation to climate change, decision-making, and transformative social change. His experience studying social systems and how they change spans multiple topics and continents, ranging from poverty alleviation in the Middle East to human adaptation to policy and climate change in the United States and Ukraine. A Fulbright Award recipient, Garry’s theoretical and applied research has been funded by the United Nations, the World Bank, and the USDA. He has published in various journals, including Sustainability Science, PNAS, and Nature Climate Change.
Research Interests
agent-based modeling, cognition
Peer reviewed Multilevel Group Selection I
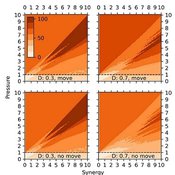
Garry Sotnik Thaddeus Shannon Wayne W. Wakeland | Published Tuesday, April 21, 2020 | Last modified Saturday, July 03, 2021New theoretical agent-based model of population-wide adoption of prosocial common-pool behavior with four parameters (initial percent of adopters, pressure to change behavior, synergy from behavior, and population density); dynamics in behavior, movement, freeriding, and group composition and size; and emergence of multilevel group selection. Theoretical analysis of model’s dynamics identified six regions in model’s parameter space, in which pressure-synergy combinations lead to different outcomes: extinction, persistence, and full adoption. Simulation results verified the theoretical analysis and demonstrated that increases in density reduce number of pressure-synergy combinations leading to population-wide adoption; initial percent of contributors affects underlying behavior and final outcomes, but not size of regions or transition zones between them; and random movement assists adoption of prosocial common-pool behavior.
Co-evolution of mental models among socially learning agents
Garry Sotnik | Published Sunday, October 14, 2018The model simulates seven agents engaging in collective action and inter-network social learning. The objective of the model is to demonstrate how mental models of agents can co-evolve through a complex relationship among factors influencing decision-making, such as access to knowledge and personal- and group-level constraints.
Under development.