About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers at all levels engage in the establishment and adoption of community standards and good practices for developing and sharing computational models. Model authors can freely publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library alongside narrative documentation, open science metadata, and other emerging open science norms that facilitate software citation, reproducibility, interoperability, and reuse. Model authors can also request peer review of their computational models to receive a DOI.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with additional detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 772 results netlogo clear
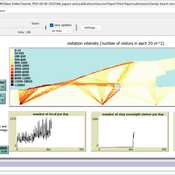
Sandy Beach Visitor Flow: An Agent-Based Model
Elham Bakhshianlamouki | Published Thursday, March 14, 2024The model is intended to simulate visitor spatial and temporal dynamics, encompassing their numbers, activities, and distribution along a coastline influenced by beach landscape design. Our primary focus is understanding how the spatial distribution of services and recreational facilities (e.g., beach width, entrance location, recreational facilities, parking availability) impacts visitation density. Our focus is not on tracking the precise visitation density but rather on estimating the areas most affected by visitor activity. This comprehension allows for assessing the diverse influences of beach layouts on spatial visitor density and, consequently, on the landscape’s biophysical characteristics (e.g., vegetation, fauna, and sediment features).
Agent-based tax evasion model for investigating impacts of public disclosure
Hiroyuki Sano | Published Thursday, March 14, 2024The model explores the impact of public disclosure on tax compliance among diverse agents, including individual taxpayers and a tax authority. It incorporates heterogeneous preferences and income endowments among taxpayers, captured through a utility function that considers psychic costs subtracted from expected pecuniary utility. These costs include moral, reciprocity, and stigma costs associated with norm violations, leading to variations in taxpayers’ risk attitudes and related parameters. The tax authority’s attributes, such as the frequency of random audits, penalty rate, and the choice between partial or full disclosure, remain fixed throughout the simulation. Income endowments and preference parameters are randomly assigned to taxpayers at the outset.
Taxpayers maximize their expected utility by reporting income, taking into account tax, penalty, and audit rates. They make annual decisions based on their own and their peers’ behaviors from the previous year. Taxpayers indirectly interact at the societal level through public disclosure conducted by the tax authority, exchanging tax information among peers. Each period in the simulation collects data on total reported income, average compliance rates per income group, distribution of compliance rates, counts of compliers, full evaders, partial evaders, and the numbers of taxpayers experiencing guilt and anger. The model evaluates whether public disclosure positively or negatively impacts compliance rates and quantifies this impact based on aggregated individual reporting behaviors.
Peer reviewed HUMLAND: HUMan impact on LANDscapes agent-based model
Anastasia Nikulina Katharine MacDonald Anhelina Zapolska Maria Antonia Serge Marco Davoli Dave van Wees Fulco Scherjon | Published Monday, October 16, 2023The HUMan impact on LANDscapes (HUMLAND) model has been developed to track and quantify the intensity of different impacts on landscapes at the continental level. This agent-based model focuses on determining the most influential factors in the transformation of interglacial vegetation with a specific emphasis on burning organized by hunter-gatherers. HUMLAND integrates various spatial datasets as input and target for the agent-based model results. Additionally, the simulation incorporates recently obtained continental-scale estimations of fire return intervals and the speed of vegetation regrowth. The obtained results include maps of possible scenarios of modified landscapes in the past and quantification of the impact of each agent, including climate, humans, megafauna, and natural fires.
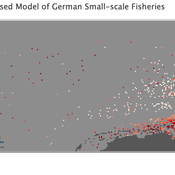
Peer reviewed Viable North Sea (ViNoS): A NetLogo Agent-based Model of German Small-scale Fisheries
Carsten Lemmen Sascha Hokamp Serra Örey Wolfgang Nikolaus Probst Jürgen Scheffran Jieun Seo Verena Mühlberger | Published Thursday, May 25, 2023 | Last modified Tuesday, December 05, 2023Viable North Sea (ViNoS) is an Agent-based Model of the German North Sea Small-scale Fisheries in a Social-Ecological Systems framework focussing on the adaptive behaviour of fishers facing regulatory, economic, and resource changes. Small-scale fisheries are an important part both of the cultural perception of the German North Sea coast and of its fishing industry. These fisheries are typically family-run operations that use smaller boats and traditional fishing methods to catch a variety of bottom-dwelling species, including plaice, sole, and brown shrimp. Fisheries in the North Sea face area competition with other uses of the sea – long practiced ones like shipping, gas exploration and sand extractions, and currently increasing ones like marine protection and offshore wind farming. German authorities have just released a new maritime spatial plan implementing the need for 30% of protection areas demanded by the United Nations High Seas Treaty and aiming at up to 70 GW of offshore wind power generation by 2045. Fisheries in the North Sea also have to adjust to the northward migration of their established resources following the climate heating of the water. And they have to re-evaluate their economic balance by figuring in the foreseeable rise in oil price and the need for re-investing into their aged fleet.
An age and/or gender-based division of labor during the Last Glacial Maximum in Iberia through rabbit hunting
Samuel Seuru Ariane Burke Liliana Perez | Published Thursday, February 29, 2024Many archaeological assemblages from the Iberian Peninsula dated to the Last Glacial Maximum contain large quantities of European rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus) remains with an anthropic origin. Ethnographic and historic studies report that rabbits may be mass-collected through warren-based harvesting involving the collaborative participation of several persons.
We propose and implement an Agent-Based Model grounded in the Optimal Foraging Theory and the Diet Breadth Model to examine how different warren-based hunting strategies influence the resulting human diets.
…
Peer reviewed The Viability of the Social-Ecological Agroecosystem (ViSA) Spatial Agent-based Model
Mostafa Shaaban | Published Friday, June 03, 2022ViSA simulates the decision behaviors of different stakeholders showing demands for ecosystem services (ESS) in agricultural landscape. The lack of sufficient supply of ESSs triggers stakeholders to apply different management options to increase their supply. However, while attempting to reduce the supply-demand gap, conflicts arise among stakeholders due to the tradeoff nature of some ESS. ViSA investigates conditions and scenarios that can minimize such supply-demand gap while reducing the risk of conflicts by suggesting different mixes of management options and decision rules.
Peer reviewed Co-adoption of low-carbon household energy technologies
Mart van der Kam Maria Lagomarsino Elie Azar Ulf Hahnel David Parra | Published Tuesday, August 29, 2023 | Last modified Friday, February 23, 2024The model simulates the diffusion of four low-carbon energy technologies among households: photovoltaic (PV) solar panels, electric vehicles (EVs), heat pumps, and home batteries. We model household decision making as the decision marking of one person, the agent. The agent decides whether to adopt these technologies. Hereby, the model can be used to study co-adoption behaviour, thereby going beyond traditional diffusion models that focus on the adop-tion of single technologies. The combination of these technologies is of particular interest be-cause (1) using the energy generated by PV solar panels for EVs and heat pumps can reduce emissions associated with transport and heating, respectively, and (2) EVs, heat pumps, and home batteries can help to integrate PV solar panels in local electricity grids by offering flexible demand (EVs and heat pumps) and energy storage (home batteries and EVs), thereby reducing grid impacts and associated upgrading costs.
The purpose of the model is to represent realistic adoption and co-adoption behaviour. This is achieved by grounding the decision model on the risks-as-feelings model (Loewenstein et al., 2001), theory from environmental and social psychology, and empirically informing agent be-haviour by survey-data among 1469 people in the Swiss region Romandie.
The model can be used to construct scenarios for the diffusion of the four low-carbon energy technologies depending on different contexts, and as a virtual experimentation environment for ex ante evaluation of policy interventions to stimulate adoption and co-adoption.
Peer reviewed MADTOR: Model for Assessing Drug Trafficking Organizations Resilience
Deborah Manzi | Published Friday, February 23, 2024Criminal organizations operate in complex changing environments. Being flexible and dynamic allows criminal networks not only to exploit new illicit opportunities but also to react to law enforcement attempts at disruption, enhancing the persistence of these networks over time. Most studies investigating network disruption have examined organizational structures before and after the arrests of some actors but have disregarded groups’ adaptation strategies.
MADTOR simulates drug trafficking and dealing activities by organized criminal groups and their reactions to law enforcement attempts at disruption. The simulation relied on information retrieved from a detailed court order against a large-scale Italian drug trafficking organization (DTO) and from the literature.
The results showed that the higher the proportion of members arrested, the greater the challenges for DTOs, with higher rates of disrupted organizations and long-term consequences for surviving DTOs. Second, targeting members performing specific tasks had different impacts on DTO resilience: targeting traffickers resulted in the highest rates of DTO disruption, while targeting actors in charge of more redundant tasks (e.g., retailers) had smaller but significant impacts. Third, the model examined the resistance and resilience of DTOs adopting different strategies in the security/efficiency trade-off. Efficient DTOs were more resilient, outperforming secure DTOs in terms of reactions to a single, equal attempt at disruption. Conversely, secure DTOs were more resistant, displaying higher survival rates than efficient DTOs when considering the differentiated frequency and effectiveness of law enforcement interventions on DTOs having different focuses in the security/efficiency trade-off.
Overall, the model demonstrated that law enforcement interventions are often critical events for DTOs, with high rates of both first intention (i.e., DTOs directly disrupted by the intervention) and second intention (i.e., DTOs terminating their activities due to the unsustainability of the intervention’s short-term consequences) culminating in dismantlement. However, surviving DTOs always displayed a high level of resilience, with effective strategies in place to react to threatening events and to continue drug trafficking and dealing.
Peer reviewed A Bayesian Nash Equilibrium (BNE)-informed ABM for pedestrian evacuation in different constricted spaces
Yiyu Wang Jiaqi Ge Alexis Comber | Published Wednesday, October 11, 2023This BNE-informed ABM ultimately aims to provide a more realistic description of complicated pedestrian behaviours especially in high-density and life-threatening situations. Bayesian Nash Equilibrium (BNE) was adopted to reproduce interactive decision-making process among rational and game-playing agents. The implementations of 3 behavioural models, which are Shortest Route (SR) model, Random Follow (RF) model, and BNE model, make it possible to simulate emergent patterns of pedestrian behaviours (e.g. herding and self-organised queuing behaviours, etc.) in emergency situations.
According to the common features of previous mass trampling accidents, a series of simulation experiments were performed in space with 3 types of barriers, which are Horizontal Corridors, Vertical Corridors, and Random Squares, standing for corridors, bottlenecks and intersections respectively, to investigate emergent behaviours of evacuees in varied constricted spatial environments. The output of this ABM has been available at https://data.mendeley.com/datasets/9v4byyvgxh/1.
Digital Mobility Model (DMM)
njiang13 | Published Thursday, February 01, 2024 | Last modified Friday, February 02, 2024The purpose of the Digital Mobility Model (DMM) is to explore how a society’s adoption of digital technologies can impact people’s mobilities and immobilities within an urban environment. Thus, the model contains dynamic agents with different levels of digital technology skills, which can affect their ability to access urban services using digital systems (e.g., healthcare or municipal public administration with online appointment systems). In addition, the dynamic agents move within the model and interact with static agents (i.e., places) that represent locations with different levels of digitalization, such as restaurants with online reservation systems that can be considered as a place with a high level of digitalization. This indicates that places with a higher level of digitalization are more digitally accessible and easier to reach by individuals with higher levels of digital skills. The model simulates the interaction between dynamic agents and static agents (i.e., places), which captures how the gap between an individual’s digital skills and a place’s digitalization level can lead to the mobility or immobility of people to access different locations and services.
Displaying 10 of 772 results netlogo clear