About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers at all levels engage in the establishment and adoption of community standards and good practices for developing and sharing computational models. Model authors can freely publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library alongside narrative documentation, open science metadata, and other emerging open science norms that facilitate software citation, reproducibility, interoperability, and reuse. Model authors can also request peer review of their computational models to receive a DOI.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with additional detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 8 of 98 results for 'Michael E Wolf-Branigin'
Comparing agent-based models on experimental data of irrigation games
Jacopo Baggio Marco Janssen | Published Tuesday, July 02, 2013 | Last modified Wednesday, July 03, 2013Comparing 7 alternative models of human behavior and assess their performance on a high resolution dataset based on individual behavior performance in laboratory experiments.
Modeling financial networks based on interpersonal trust
Anna Klabunde Michael Roos | Published Wednesday, May 29, 2013 | Last modified Thursday, November 28, 2013We build a stylized model of a network of business angel investors and start-up entrepreneurs. Decisions are based on trust as a decision making tool under true uncertainty.
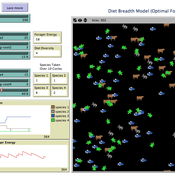
Diet breadth model from Optimal Foraging Theory (Human Behavioral Ecology)
C Michael Barton | Published Wednesday, November 26, 2008 | Last modified Thursday, March 12, 2015Diet breadth is a classic optimal foraging theory (OFT) model from human behavioral ecology (HBE). Different resources, ranked according to their food value and processing costs, are distributed in th
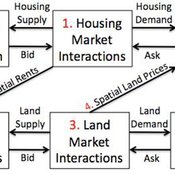
Coupled Housing and Land Markets (CHALMS)
Nicholas Magliocca Virginia Mcconnell Margaret Walls | Published Friday, November 02, 2012 | Last modified Monday, October 27, 2014CHALMS simulates housing and land market interactions between housing consumers, developers, and farmers in a growing ex-urban area.
Alternative scenarios of green consumption in Italy: an empirically grounded model.
Giangiacomo Bravo Elena Vallino Alessandro K Cerutti Maria Beatrice Pairotti | Published Thursday, March 28, 2013 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013We provide a full description of the model following the ODD protocol (Grimm et al. 2010) in the attached document. The model is developed in NetLogo 5.0 (Wilenski 1999).
Peer reviewed Hominin ecodynamics v.1
C Michael Barton | Published Saturday, October 01, 2011 | Last modified Friday, March 28, 2014Biobehavioral interactions between two populations under different movement strategies.
ABSAM model
Marcin Wozniak | Published Monday, August 29, 2016 | Last modified Tuesday, November 08, 2016ABSAM model is an agent-based search and matching model of the local labor market. There are four types of agents in the economy, which cooperate in the artificial world, where behavioral rules were extracted from the labor market search theory.
Patch choice model from Optimal Foraging Theory (Human Behavioral Ecology)
C Michael Barton | Published Saturday, November 22, 2008 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013NetLogo model of patch choice model from optimal foraging theory (human behavioral ecology).
Displaying 8 of 98 results for 'Michael E Wolf-Branigin'